Software I love
WinRAR: The Ultimate Guide to File Compression and Extraction
Imagine reducing megabytes of data into mere kilobytes with a single click. Whether you’re sending an important document or managing extensive multimedia libraries, WinRAR stands as a powerful ally in your digital arsenal. Dive into this comprehensive guide to uncover everything you need to know about mastering file compression and extraction with WinRAR.
Introduction
WinRAR is not just another file compression tool; it’s a versatile software solution trusted by millions worldwide. Developed by Eugene Roshal and launched in 1995, WinRAR has evolved to support various archive formats, ensuring that users can efficiently store, share, and manage their data across different platforms. This guide explores WinRAR’s functionalities, advantages, and how it compares to other compression tools, providing you with the knowledge to make the most of its features.
What is WinRAR?
WinRAR is a robust file compression and archiving utility designed to reduce the size of files and folders, making them easier to store and share. Since its inception, WinRAR has become a staple for both personal and professional use, thanks to its comprehensive features and user-friendly interface.
WinRAR supports a multitude of archive formats, including:
- RAR: Its proprietary format known for high compression ratios.
- ZIP: A widely recognized format compatible with numerous applications.
- 7-Zip, Tar, GZ, and more: Ensuring versatility in handling various file types.
Key characteristics that set WinRAR apart include:
- Compression Efficiency: Advanced algorithms that minimize file sizes without significant quality loss.
- Security Features: AES-256 encryption and password protection to safeguard sensitive data.
- Recovery Tools: Ability to repair corrupted archives using recovery records.
- Multi-Volume Archives: Splitting large archives into manageable sizes for easier distribution.
Additionally, WinRAR’s seamless integration with Windows Explorer allows users to perform compression and extraction tasks directly from the context menu, enhancing overall productivity. Whether you’re archiving documents, compressing multimedia files, or securing sensitive information, WinRAR provides the tools necessary for efficient file management.
Why Use WinRAR for File Compression?
Choosing the right file compression tool can significantly impact your data management efficiency. WinRAR offers numerous advantages that make it a preferred option for users across various domains.
1. Superior Compression Ratios:
WinRAR’s proprietary RAR format often achieves smaller file sizes compared to traditional ZIP archives. This efficiency is particularly beneficial when dealing with large files or extensive data sets, as it allows for optimized storage and quicker file transfers.
2. Extensive Format Support:
While WinRAR excels with RAR and ZIP formats, it also supports a broad range of other formats like TAR, GZ, and ISO. This versatility ensures compatibility with different systems and applications, catering to diverse user requirements.
3. Enhanced Security Measures:
Security is paramount in today’s digital landscape. WinRAR provides robust protection through password encryption and AES-256 standards, ensuring that your sensitive files remain inaccessible to unauthorized users. Additionally, the ability to encrypt file names adds an extra layer of security.
4. Ease of Use and Integration:
WinRAR’s intuitive interface and seamless integration with Windows Explorer simplify the compression and extraction processes. Users can easily access WinRAR features via the context menu, eliminating the need for navigating through complex menus.
5. Data Integrity and Recovery:
One of WinRAR’s standout features is its ability to repair corrupted archives using recovery records. This capability is crucial for preventing data loss, especially when handling important or irreplaceable files.
6. Multi-Volume Archives:
Splitting large archives into smaller parts is essential for easier sharing and storage, especially when dealing with limitations in file sizes for emails or storage devices. WinRAR facilitates the creation of multi-volume archives, providing flexibility in managing large files.
In comparison to other compression tools, WinRAR balances speed and compression efficiency, making it suitable for both casual users and professionals who require reliable and secure file compression solutions.

Key Features of WinRAR
WinRAR is packed with features that enhance its functionality beyond mere file compression. These features cater to a wide range of user needs, making it a versatile tool for both personal and professional use.
1. Advanced Compression Algorithms:
WinRAR utilizes sophisticated compression algorithms such as RAR and ZIP, providing high compression ratios while maintaining data integrity. This ensures that files are reduced in size efficiently without compromising quality.
2. Strong Encryption Options:
Security is a fundamental aspect of WinRAR. It offers AES-256 encryption, one of the most secure encryption standards, ensuring that compressed files are not easily accessible without the correct password. This feature is crucial for protecting sensitive or confidential information.
3. Recovery and Repair Capabilities:
WinRAR can automatically repair corrupted archives using recovery records embedded within the archive during its creation. This feature is invaluable for recovering data from damaged files, minimizing the risk of complete data loss.
4. Multi-Volume Archive Creation:
Traveling or sharing large files can be challenging due to size restrictions. WinRAR addresses this by allowing users to split archives into multiple parts, making it easier to distribute large files across different storage media or online platforms.
5. Self-Extracting Archives:
For users who need to share compressed files with recipients who do not have WinRAR, the software can create self-extracting archives. These are executable files that can extract their contents without requiring additional software, enhancing user convenience and accessibility.
6. Integration with Windows Explorer:
WinRAR integrates seamlessly with the Windows operating system, providing context menu options for compressing and extracting files directly from the file explorer. This integration streamlines the workflow, saving time and effort.
7. File Association Settings:
Users can customize file associations to ensure that specific file types are automatically handled by WinRAR. This feature simplifies file management, allowing for faster access and organization.
8. Extensive Format Support:
In addition to RAR and ZIP, WinRAR supports a variety of other formats such as TAR, GZ, and ISO, making it a versatile tool for handling different types of compressed files.
Comparison Table of Key Features:
| Feature | WinRAR | 7-Zip | WinZip |
|---|---|---|---|
| **Compression Formats** | RAR, ZIP, TAR, GZ, ISO | 7z, ZIP, TAR, GZ, ISO | ZIP, RAR (extract only), 7z |
| **Encryption** | AES-256 | AES-256 | AES-256 |
| **Recovery Records** | Yes | No | Limited |
| **Self-Extracting Archives** | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| **File Association** | Highly configurable | Basic configuration | Limited configuration |
| **Platform Compatibility** | Windows, macOS, Linux | Primarily Windows | Windows, Mac |
Table 1: Feature Comparison Between WinRAR, 7-Zip, and WinZip.
WinRAR’s comprehensive feature set, combined with its efficiency and security, makes it an essential tool for anyone requiring reliable file compression and management. Its ability to handle various formats and integrate seamlessly with the operating system enhances its usability, making it a preferred choice over other compression tools.
How to Download and Install WinRAR
Ensuring that WinRAR is downloaded from a secure source is crucial for maintaining your system’s integrity and avoiding malicious software. This section outlines the safest methods to download and install WinRAR on your Windows or Mac system.
Where to Download WinRAR Safely
Downloading WinRAR from a legitimate and secure source is paramount to avoid malware and ensure you receive the latest version of the software. Follow these steps for a safe download:
1. Official Website:
Always download WinRAR from the official RARLAB website (www.rarlab.com). This guarantees that you are accessing the most recent and unaltered version of the software.
2. Avoid Third-Party Sites:
Refrain from downloading WinRAR from unofficial websites or third-party distributors. These sources may bundle unwanted software or malware with the WinRAR installer, posing security risks.
3. Verify Download Links:
Make sure the download links are correct by checking the website URL. Authentic links from the official site will typically follow the format: https://www.win-rar.com/download.html
4. Check Digital Signatures:
After downloading the installer, verify its digital signature to ensure its authenticity. Right-click the file, select Properties, and navigate to the Digital Signatures tab to confirm it is from RARLAB.
5. Use a Secure Network:
Download WinRAR over a secure and trusted internet connection to prevent interception or tampering by malicious actors.
Following these steps helps ensure that your WinRAR download is safe, secure, and free from any harmful software.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide for Windows and Mac
Installing WinRAR is a straightforward process, whether you’re using Windows or macOS. Follow these detailed steps to get started:
For Windows:
- Download WinRAR:
- Visit the official WinRAR website at www.win-rar.com.
- Navigate to the “Downloads” section.
- Select the appropriate version for your Windows operating system (32-bit or 64-bit).
- Run the Installer:
- Locate the downloaded setup file, usually in your “Downloads” folder.
- Double-click the setup file to launch the installer.
- Follow Installation Prompts:
- Choose your preferred language and click “OK.”
- Click “Install” to begin the installation process.
- Select the destination folder where WinRAR will be installed or use the default path.
- Customize Installation (Optional):
- Choose file associations if you want WinRAR to manage certain archive formats by default.
- Decide whether to create desktop shortcuts for easy access.
- Complete Installation:
- Once the installation is complete, click “Done.”
- WinRAR should now be installed and ready for use on your Windows system.
For Mac:
- Download WinRAR:
- Go to the official website and locate the Mac version of WinRAR.
- Run the Installer:
- Open the downloaded .dmg file to mount the installer.
- Follow Installation Prompts:
- Drag the WinRAR icon into the Applications folder.
- Finalize Installation:
- Eject the installer disk image.
- Launch WinRAR from the Applications folder to begin using the software.
System Requirements Summary Table:
| Requirement | Windows | Mac | Linux |
|---|---|---|---|
| **OS** | Windows 11/10/… | macOS 10.12+ | Various Linux |
| **Processor** | 1 GHz+ | Intel processor | 1 GHz+ |
| **RAM** | 512 MB+ | 512 MB+ | 512 MB+ |
| **Storage** | 150 MB+ free | 150 MB+ free | 150 MB+ free |
| **Other Needs** | .NET Framework | Administrator | Dependencies |
Following these steps ensures a smooth installation process for WinRAR on both Windows and Mac systems, allowing you to efficiently manage your file compression and extraction tasks.
System Requirements for Running WinRAR
Before installing WinRAR, it’s essential to ensure that your system meets the necessary requirements to run the software effectively. Here’s a breakdown of the system specifications needed for different operating systems:
For Windows:
- Operating System:
- Windows 11, 10, 8, 7, Vista, XP
- Processor:
- 1 GHz or faster processor
- Memory (RAM):
- Minimum 512 MB (1 GB recommended)
- Storage:
- At least 150 MB of free disk space
- Additional Requirements:
- .NET Framework 2.0 or later
For Mac:
- Operating System:
- macOS 10.12 (Sierra) or later
- Processor:
- Intel processor
- Memory (RAM):
- Minimum 512 MB (1 GB recommended)
- Storage:
- At least 150 MB of free disk space
- Additional Requirements:
- Administrative privileges for installation
For Linux:
- Operating System:
- Various Linux distributions, including Debian, Ubuntu, Fedora
- Processor:
- 1 GHz or faster processor
- Memory (RAM):
- Minimum 512 MB
- Storage:
- At least 150 MB of free disk space
- Additional Requirements:
- Dependencies such as libz.so, libcrypto.so (specific versions may vary)
Compatibility Considerations:
- File Formats Supported:
- RAR, ZIP, 7-Zip, TAR, GZ, ISO, and more
- User Permissions:
- Read and write permissions for accessing and modifying files
Performance Recommendations:
- RAM:
- More RAM can enhance performance, especially when handling large archives or multi-volume archives.
- Processor:
- A faster processor can reduce compression and extraction times.
- Disk Space:
- Sufficient disk space ensures smooth operation without interruptions during the compression or extraction process.
Visual Representation:
| Requirement | Windows | Mac | Linux |
|---|---|---|---|
| **OS** | Windows 11/10/… | macOS 10.12+ | Various Linux |
| **Processor** | 1 GHz+ | Intel processor | 1 GHz+ |
| **RAM** | 512 MB+ | 512 MB+ | 512 MB+ |
| **Storage** | 150 MB+ free | 150 MB+ free | 150 MB+ free |
| **Other Needs** | .NET Framework | Administrator | Dependencies |
Ensuring your system meets these requirements will allow WinRAR to function optimally, providing a seamless experience in managing your file compression and extraction tasks.
Features and Benefits of WinRAR
Having successfully downloaded and installed WinRAR, it’s time to explore its extensive features and understand how they can benefit your file management needs. WinRAR offers a suite of tools designed to improve efficiency, security, and ease of use, making it an indispensable asset for both casual users and professionals.
Compressing Files to Reduce Storage Space
One of WinRAR’s primary functions is to compress files, thereby reducing their size to save storage space. This feature is invaluable in various scenarios, such as:
1. Efficient Data Storage:
By compressing large files and folders, users can maximize their storage capacity on hard drives, SSDs, and USB flash drives. This is particularly useful for managing extensive multimedia libraries, large datasets, or numerous documents.
2. Fast File Transfer:
Smaller file sizes result in quicker upload and download times. Whether sending files via email, uploading to cloud storage services, or transferring over a network, compressed files can be handled more efficiently, saving time and bandwidth.
3. Organization and Management:
Consolidating multiple files into a single archive simplifies file organization. Users can group related files together, making it easier to locate and manage them, especially when dealing with complex projects or large volumes of data.
4. Cost Savings:
Reducing file sizes can lead to cost savings, particularly when dealing with limited storage plans or bandwidth constraints. Compressed files take up less space on cloud storage platforms, potentially reducing storage costs.
5. Backup and Archiving:
Compressing files before backing them up ensures that backups are more manageable and consume less space. This can lead to more frequent backups as they require less time and storage resources.
Benefits Table:
| Activity | Benefit of Compression |
|---|---|
| **Data Storage** | Maximizes available storage space |
| **File Transfer** | Speeds up upload and download times |
| **File Organization** | Simplifies management of multiple files |
| **Cost Efficiency** | Reduces storage and bandwidth costs |
| **Backup Archiving** | Makes backups more manageable and space-efficient |
Example Use Case:
Consider a photographer who needs to store thousands of high-resolution images. Compressing these images into RAR archives not only saves significant disk space but also simplifies the process of transferring the files to clients or other storage devices. By using WinRAR’s compression features, the photographer ensures efficient use of storage and faster file sharing without compromising the quality of the images.
In summary, WinRAR’s compression capabilities offer a wide array of benefits that enhance data management, streamline file transfers, and optimize storage usage, making it an essential tool for anyone handling large amounts of data.

Extracting Zip, Rar, and Other Archive Formats
WinRAR’s extraction capabilities are designed to handle various archive formats with ease and efficiency. Understanding how to extract files effectively ensures seamless access to your data.
1. Wide Format Support:
WinRAR supports an extensive range of archive formats, including RAR, ZIP, 7z, TAR, GZ, and ISO. This flexibility ensures that users can extract files from virtually any compressed archive they encounter, regardless of the format used.
2. User-Friendly Extraction Options:
WinRAR offers multiple extraction options to cater to different user needs. Options such as “Extract Here” allow users to quickly unpack files in their current directory, while “Extract to [folder name]” organizes the extracted content into a new folder, enhancing file management.
3. Password-Protected Archives:
For security-conscious users, WinRAR can handle password-protected archives. When extracting such files, users are prompted to enter the correct password, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access the contents.
4. Enhanced Compatibility:
WinRAR’s ability to handle multiple formats ensures compatibility across different platforms and systems. Whether receiving an archive from a colleague using a different compression tool or encountering various formats in digital transfers, WinRAR provides a seamless extraction experience.
5. Batch Extraction:
Users can extract multiple archives simultaneously using WinRAR’s batch extraction feature. This is particularly useful when dealing with numerous files, saving time and effort by processing them in one operation.
Step-by-Step Extraction Process:
- Locate the Archive:
- Find the ZIP, RAR, or other archive file you wish to extract.
- Right-Click the Archive:
- Right-click on the file to open the context menu.
- Choose Extraction Option:
- Select “Extract Here” to unpack the files in the current directory.
- Alternatively, choose “Extract to [folder name]” to extract the contents into a new folder.
- Enter Password (If Required):
- If the archive is password-protected, enter the correct password when prompted.
- Wait for Extraction to Complete:
- Depending on the archive size and system performance, the extraction process may take a few moments.
Benefits Table:
| Extraction Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| **Wide Format Support** | Access files from various archive types |
| **Password Handling** | Securely access protected archives |
| **Batch Processing** | Efficiently extract multiple archives |
| **Folder Organization** | Maintain structured file directories |
| **Compatibility** | Ensure access across different platforms |
Example Use Case:
A software engineer receives a compressed RAR archive containing various code modules from a collaborator. Using WinRAR, the engineer right-clicks the archive, selects “Extract to [folder name],” and accesses all the files within seconds. If the archive is password-protected, the engineer simply enters the secure password provided, ensuring that the contents remain protected during transmission.
By mastering the extraction process with WinRAR, users can swiftly and securely access their data, enhancing productivity and data management efficiency.
Creating Password-Protected Archives for Security
Securing sensitive data is a critical concern in today’s digital age. WinRAR offers robust features to protect your files, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access the contents of your archives.
1. AES-256 Encryption:
WinRAR utilizes Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) with a 256-bit key, providing military-grade encryption for your archives. This level of security ensures that your data remains confidential and protected from unauthorized access.
2. Password Protection:
Creating password-protected archives is simple with WinRAR. Users can set a password during the archive creation process, requiring anyone who attempts to extract the files to enter the correct password.
3. Encrypt File Names:
In addition to encrypting the contents, WinRAR allows users to encrypt file names. This feature prevents anyone from identifying the contents of the archive without the password, adding an extra layer of security.
4. Protection Against Unauthorized Access:
Password-protected archives safeguard sensitive information such as financial documents, personal data, and confidential business files. This is especially important when sharing files over insecure channels like email or online storage.
5. Ease of Use:
Despite the robust security features, creating password-protected archives with WinRAR is user-friendly. The encryption options are accessible during the archiving process, allowing users to set up security with minimal steps.
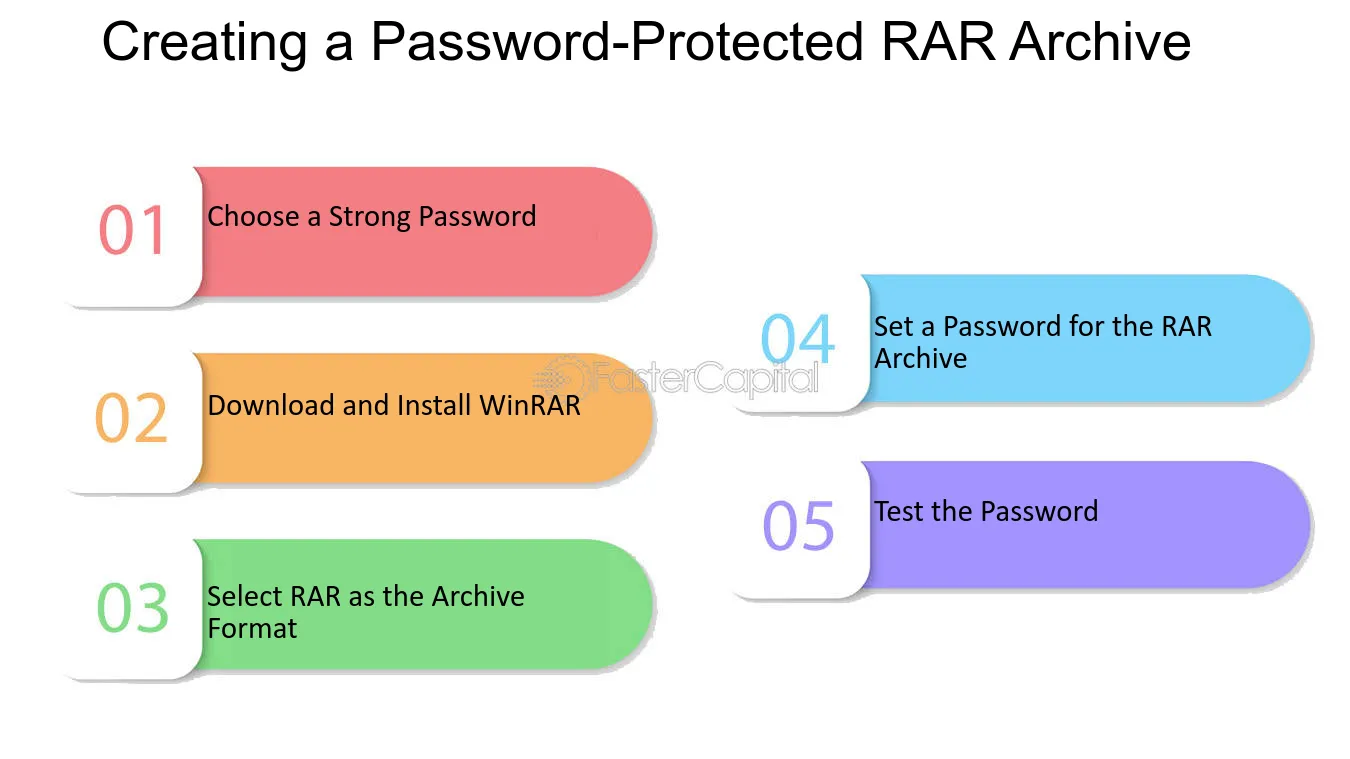
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Password-Protected Archive:
- Select Files/Folders to Compress:
- Right-click on the selected files or folders you wish to compress.
- Choose ‘Add to Archive’:
- From the context menu, select “Add to archive” to open the compression settings window.
- Set Archive Format:
- Choose RAR as the archive format from the dropdown menu.
- Access Encryption Settings:
- Click the “Set password…” button within the archiving options.
- Enter and Confirm Password:
- Input your desired password and confirm it by typing it again in the verification field.
- Enable ‘Encrypt File Names’ (Optional):
- For added security, check the box labeled “Encrypt file names.”
- Finalize and Create Archive:
- Click “OK” to create the password-protected archive. The archive will now require the password for extraction.
Benefits of Password Protection:
- Data Security:
Protects sensitive information from unauthorized access, ensuring confidentiality. - Integrity Maintenance:
Prevents unauthorized modification or tampering with the archive contents. - Compliance Requirements:
Helps in meeting data protection standards and regulations by safeguarding sensitive data.
Security Features Table:
| Security Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| **Password Encryption** | Secures access to archive contents |
| **AES-256 Encryption** | Provides strong, industry-standard encryption |
| **Encrypt File Names** | Conceals file names for added security |
| **Password Strength** | Enhances overall security with strong passwords |
| **User Control** | Users determine the level of security needed |
Example Use Case:
A legal professional needs to send confidential case files to a colleague. By compressing the files into a RAR archive and adding password protection, the professional ensures that only the intended recipient, who possesses the password, can access the sensitive information.
Best Practices for Password Protection:
- Use Strong Passwords:
Combine uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters to create a robust password. - Avoid Common Passwords:
Steer clear of easily guessable passwords such as “password123” or “admin.” - Store Passwords Securely:
Use a password manager to keep track of your passwords without compromising security. - Communicate Passwords Securely:
Share the password through a separate communication channel (e.g., phone or separate email) to reduce the risk of interception. - Regularly Update Passwords:
Change passwords periodically to maintain the security of your archives.
Creating password-protected archives with WinRAR offers peace of mind by securing your valuable data, making it a fundamental practice for anyone handling sensitive information.
Splitting Large Files into Smaller Parts for Easy Sharing
Handling large files can be cumbersome, especially when sharing them over platforms with file size limitations or storing them on media with limited capacity. WinRAR addresses this challenge with its multi-volume archive feature, allowing users to split large archives into smaller, more manageable parts.
1. Simplified Sharing:
Splitting large files into smaller volumes makes it easier to share them via email, messaging apps, or cloud storage services that impose size restrictions. Each part can be sent separately, ensuring that the entire file can be reconstructed by the recipient.
2. Enhanced Storage Flexibility:
Smaller archive parts can be stored on various media such as CDs, DVDs, or USB drives, overcoming storage capacity constraints. This flexibility is particularly useful when dealing with archival purposes or backing up data across multiple storage devices.
3. Error Management:
Handling smaller volumes reduces the risk of data loss or corruption. If one part is damaged or unreadable, only that fragment is affected, making it easier to repair or replace without compromising the entire archive.
4. Customizable Volume Sizes: WinRAR allows users to specify the size of each archive part based on their requirements. Whether you need parts suitable for CD-ROMs, DVDs, or specific file sharing platforms, WinRAR offers the flexibility to customize accordingly.
5. Automation and Efficiency: The process of splitting archives into multiple parts is automated, saving users time and effort. The creation of multi-volume archives is seamless and integrated into the overall archiving process.
Step-by-Step Guide to Splitting Large Files:
- Select Files/Folders to Compress:
- Right-click on the desired files or folders and choose “Add to archive.”
- Choose Archive Format:
- Select the desired archive format (RAR or ZIP).
- Specify Volume Size:
- In the “Split to volumes, size” field, enter the desired size for each part (e.g., 700 MB for CD).
- Create Multi-Volume Archive:
- Proceed with the compression process. WinRAR will automatically create multiple archive files based on the specified size.
- Distribute Volumes:
- Share or store the individual archive parts as needed. To extract, all parts must be present in the same directory.
Benefits Table:
| Splitting Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| **Volume Size Customization** | Tailor archive parts to specific needs |
| **Easier Distribution** | Simplifies sharing large datasets |
| **Improved Data Integrity** | Minimizes impact of data corruption |
| **Efficient Storage** | Optimizes use of various storage media |
| **Enhanced Organization** | Maintains structure across multiple parts |
Example Use Case:
A software developer needs to distribute a large software package to multiple clients. By splitting the archive into 100 MB parts with WinRAR, the developer can ensure that each client can easily download the archive without encountering file size limits imposed by email services. Additionally, this method allows clients to download the files incrementally, simplifying the installation process.
Practical Tips:
- Consistent Naming: Ensure that split archives follow a consistent naming convention (e.g., filename.part1.rar, filename.part2.rar) to facilitate easy identification and extraction.
- Complete Set Requirement: To successfully extract a multi-volume archive, all parts must be present and located in the same directory.
- Storage Management: Label and store archive parts systematically to prevent loss or misplacement, especially when dealing with numerous volumes.
Using WinRAR to split large files into smaller parts offers significant advantages in terms of ease of sharing, storage management, and data integrity, making it a valuable feature for users handling sizeable data sets.

Repairing Corrupted Archives
Despite best efforts, archived files can sometimes become corrupted due to various reasons like incomplete downloads, software glitches, or storage media failures. WinRAR offers robust tools to repair corrupted archives, ensuring that your data remains accessible.
1. Automatic Repair Mechanism:
WinRAR includes an automatic repair feature that attempts to fix corrupted archives by leveraging recovery records embedded within the archive during its creation. This feature enhances data recovery rates, allowing users to retrieve as much information as possible from damaged files.
2. Manual Repair Process: For severely corrupted archives, WinRAR allows users to manually initiate the repair process. This involves selecting the corrupted archive, choosing the repair option, and specifying the destination for the repaired file. The software then attempts to reconstruct the archive’s contents based on available recovery data.
3. Recovery Record Integration:
When creating archives, users can add recovery records, which are additional data segments that help in repairing corrupted files. These records provide redundancy, increasing the chances of successful data recovery even if parts of the archive are damaged.
4. Compatibility with Different Formats: WinRAR’s repair functions are not limited to RAR files. The software can also attempt to repair other archive formats like ZIP, enhancing its utility across various file types.
5. Reporting and Feedback: After the repair process, WinRAR provides detailed reports on the operation’s success and what portions of the archive were successfully restored. This feedback helps users understand the extent of data recovery achieved.
Step-by-Step Repair Guide:
- Open WinRAR:
- Launch WinRAR and navigate to the location of the corrupted archive.
- Select Corrupted Archive:
- Click on the corrupted file to highlight it.
- Choose ‘Repair Archive’:
- Click on the “Tools” menu and select “Repair archive.”
- Specify Archive Type and Destination:
- Choose the appropriate archive type (RAR or ZIP).
- Select a destination folder for the repaired archive.
- Initiate Repair Process:
- Click “OK” to start the repair. WinRAR will attempt to reconstruct the archive using available recovery records.
- Review Repair Results:
- Once completed, check the destination folder for the repaired archive and review the details provided by WinRAR.
Benefits Table:
| Repair Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| **Automatic Repair** | Seamlessly recover data with minimal effort |
| **Manual Repair Option** | Provides control over the repair process |
| **Recovery Records** | Enhances repair success rates |
| **Format Flexibility** | Supports multiple archive formats |
| **Detailed Feedback** | Informs users of repair outcomes |
Example Use Case:
A user attempts to extract a RAR file containing critical project data but encounters an error message indicating corruption. By utilizing WinRAR’s repair feature, the user initiates the repair process, recovering the majority of the data even if some parts of the archive are damaged. This capability is crucial for salvaging critical information that would otherwise be lost.
Additional Considerations:
- Prevention:
Regularly adding recovery records when creating archives can increase the likelihood of successful repairs in the future. - Backup Practices:
Maintaining backups of important archives ensures that you have alternative copies in case of corruption, reducing dependency on repair tools. - Understanding Limitations:
While WinRAR is effective in many scenarios, severe corruption may still result in partial or unsuccessful data recovery. Understanding the extent of corruption can help manage expectations and seek alternative recovery methods if necessary.
In summary, WinRAR provides essential tools for repairing corrupted archives, enhancing data reliability and minimizing the risk of permanent data loss. These features reinforce WinRAR’s position as a dependable choice for file compression and management.
How to Use WinRAR Effectively
Understanding WinRAR’s features is just the beginning. To truly harness its potential, it’s essential to use the software effectively. This section provides actionable strategies and best practices to maximize your efficiency with WinRAR’s robust toolset.
How to Compress Files and Folders
Compressing files and folders with WinRAR is a straightforward process that significantly enhances your data management capabilities. By following these steps and utilizing advanced options, you can optimize your compression tasks.
1. Selecting Files and Folders:
- Open Windows Explorer and navigate to the files or folders you wish to compress.
- Use Ctrl+Click or Shift+Click to select multiple items.
2. Access ‘Add to Archive’ Option:
- Right-click on the selected items.
- Choose “Add to archive…” from the context menu to open the compression settings window.
3. Configure Archive Name and Format:
- In the Archive name field, enter a name for your compressed file.
- Select the desired archive format (RAR or ZIP) from the dropdown menu.
4. Choose Compression Method:
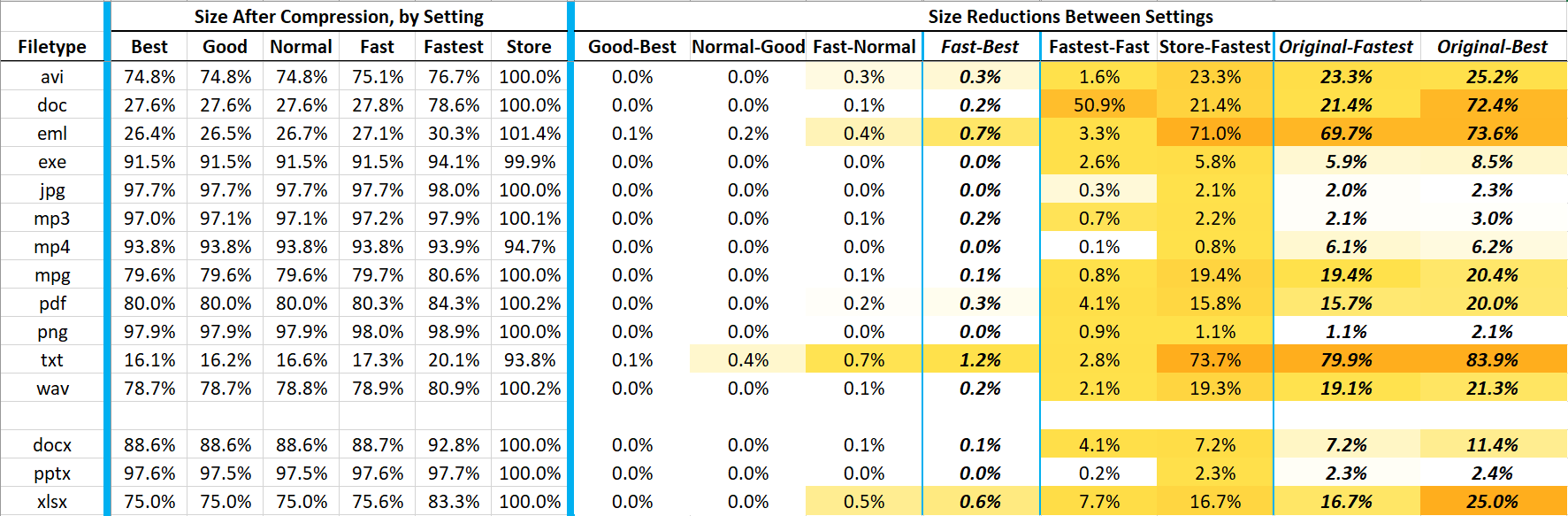
- WinRAR offers various compression methods: Store, Fastest, Fast, Normal, Good, and Best.
- Choose a method based on your needs:
- Store: No compression, fastest extraction
- Fastest: Quick compression with minimal size reduction
- Fast: Balanced speed and compression
- Normal: Standard compression ratio
- Good: Higher compression for reduced file size
- Best: Maximum compression, greatest size reduction
5. Set Volume Size (If Needed):
- For multi-volume archives, specify the size of each part (e.g., 100MB per volume).
6. Enable Compression Options:
- Solid Archive: Check this option to treat multiple files as a single data block, improving compression ratios for similar files.
- Password Protection: Click “Set password…” to protect the archive with a password.
- Recovery Record: Add a recovery record for repairing corrupted archives in the future.
7. Start Compression:
- Click “OK” to commence the compression process. WinRAR will create the archive based on your configurations.
Tips for Effective Compression:
- Organize Files: Group related files together before compression to enhance organizational efficiency.
- Select Appropriate Compression Method: Balance between speed and compression ratio based on your specific needs.
- Regularly Update WinRAR: Ensure you are using the latest version for optimal performance and security enhancements.
Benefits Table:
| Compression Setting | Benefit |
|---|---|
| **Compression Methods** | Tailor based on speed vs. size reduction |
| **Solid Archive** | Higher compression for similar files |
| **Password Protection** | Secure sensitive data |
| **Recovery Record** | Enhance archive repair capabilities |
Example Use Case:
A freelance graphic designer needs to send a project consisting of multiple high-resolution images and design files to a client. By compressing the files into a single RAR archive using the “Good” compression method, the designer reduces the total file size, facilitating faster upload and download times. Additionally, adding a password ensures that the client can securely access the files, safeguarding the designer’s work.
By following these steps and leveraging WinRAR’s advanced compression features, users can effectively manage their files, ensuring both efficiency and security in their compression tasks.
Extracting Files from Different Archive Formats
WinRAR’s extraction capabilities are designed to handle various archive formats with ease and efficiency. Understanding how to extract files effectively ensures seamless access to your data.
1. Wide Format Support:
WinRAR supports an extensive range of archive formats, including RAR, ZIP, 7z, TAR, GZ, and ISO. This flexibility ensures that users can extract files from virtually any compressed archive they encounter, regardless of the format used.
2. User-Friendly Extraction Options:
WinRAR offers multiple extraction options to cater to different user needs. Options such as “Extract Here” allow users to quickly unpack files in their current directory, while “Extract to [folder name]” organizes the extracted content into a new folder, enhancing file management.
3. Password-Protected Archives:
For security-conscious users, WinRAR can handle password-protected archives. When extracting such files, users are prompted to enter the correct password, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access the contents.
4. Enhanced Compatibility:
WinRAR’s ability to handle multiple formats ensures compatibility across different platforms and systems. Whether receiving an archive from a colleague using a different compression tool or encountering various formats in digital transfers, WinRAR provides a seamless extraction experience.
5. Batch Extraction:
Users can extract multiple archives simultaneously using WinRAR’s batch extraction feature. This is particularly useful when dealing with numerous files, saving time and effort by processing them in one operation.
Step-by-Step Extraction Process:
- Locate the Archive:
- Find the ZIP, RAR, or other archive file you wish to extract.
- Right-Click the Archive:
- Right-click on the file to open the context menu.
- Choose Extraction Option:
- Select “Extract Here” to unpack the files in the current directory.
- Alternatively, choose “Extract to [folder name]” to extract the contents into a new folder.
- Enter Password (If Required):
- If the archive is password-protected, enter the correct password when prompted.
- Wait for Extraction to Complete:
- Depending on the archive size and system performance, the extraction process may take a few moments.
Benefits Table:
| Extraction Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| **Wide Format Support** | Access files from various archive types |
| **Password Handling** | Securely access protected archives |
| **Batch Processing** | Efficiently extract multiple archives |
| **Folder Organization** | Maintain structured file directories |
| **Compatibility** | Ensure access across different platforms |
Example Use Case:
A software engineer receives a compressed RAR archive containing various code modules from a collaborator. Using WinRAR, the engineer right-clicks the archive, selects “Extract to [folder name],” and accesses all the files within seconds. If the archive is password-protected, the engineer simply enters the secure password provided, ensuring that the contents remain protected during transmission.
By mastering the extraction process with WinRAR, users can swiftly and securely access their data, enhancing productivity and data management efficiency.

Adding Password Protection to RAR Files
Securing sensitive data is a critical concern in today’s digital age. WinRAR offers robust features to protect your files, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access the contents of your archives.
1. AES-256 Encryption:
WinRAR utilizes Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) with a 256-bit key, providing military-grade encryption for your archives. This level of security ensures that your data remains confidential and protected from unauthorized access.
2. Password Protection:
Creating password-protected archives is simple with WinRAR. Users can set a password during the archive creation process, requiring anyone who attempts to extract the files to enter the correct password.
3. Encrypt File Names:
In addition to encrypting the contents, WinRAR allows users to encrypt file names. This feature prevents anyone from identifying the contents of the archive without the password, adding an extra layer of security.
4. Protection Against Unauthorized Access:
Password-protected archives safeguard sensitive information such as financial documents, personal data, and confidential business files. This is especially important when sharing files over insecure channels like email or online storage.
5. Ease of Use:
Despite the robust security features, creating password-protected archives with WinRAR is user-friendly. The encryption options are accessible during the archiving process, allowing users to set up security with minimal steps.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Password-Protected Archive:
- Select Files/Folders to Compress:
- Right-click on the selected files or folders you wish to compress.
- Choose ‘Add to Archive’:
- From the context menu, select “Add to archive” to open the compression settings window.
- Set Archive Format:
- Choose RAR as the archive format from the dropdown menu.
- Access Encryption Settings:
- Click the “Set password…” button within the archiving options.
- Enter and Confirm Password:
- Input your desired password and confirm it by typing it again in the verification field.
- Enable ‘Encrypt File Names’ (Optional):
- For added security, check the box labeled “Encrypt file names.”
- Finalize and Create Archive:
- Click “OK” to create the password-protected archive. The archive will now require the password for extraction.
Benefits of Password Protection:
- Data Security:
Protects sensitive information from unauthorized access, ensuring confidentiality. - Integrity Maintenance:
Prevents unauthorized modification or tampering with the archive contents. - Compliance Requirements:
Helps in meeting data protection standards and regulations by safeguarding sensitive data.
Security Features Table:
| Security Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| **Password Encryption** | Secures access to archive contents |
| **AES-256 Encryption** | Provides strong, industry-standard encryption |
| **Encrypt File Names** | Conceals file names for added security |
| **Password Strength** | Enhances overall security with strong passwords |
| **User Control** | Users determine the level of security needed |
Example Use Case:
A legal professional needs to send confidential case files to a colleague. By compressing the files into a RAR archive and adding password protection, the professional ensures that only the intended recipient, who possesses the password, can access the sensitive information.
Best Practices for Password Protection:
- Use Strong Passwords:
Combine uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters to create a robust password. - Avoid Common Passwords:
Steer clear of easily guessable passwords such as “password123” or “admin.” - Store Passwords Securely:
Use a password manager to keep track of your passwords without compromising security. - Communicate Passwords Securely:
Share the password through a separate communication channel (e.g., phone or separate email) to reduce the risk of interception. - Regularly Update Passwords:
Change passwords periodically to maintain the security of your archives.
Creating password-protected archives with WinRAR offers peace of mind by securing your valuable data, making it a fundamental practice for anyone handling sensitive information.

Configuring Compression Settings for Maximum Efficiency
To achieve the best possible compression efficiency, customizing WinRAR’s compression settings is essential. Tailoring these settings based on specific needs can enhance compression ratios, speed up processes, and optimize storage usage.
1. Accessing Compression Settings:
- Open WinRAR and click on “Options” in the menu bar.
- Select “Settings” and navigate to the “Compression” tab to view available options.
2. Selecting Compression Method:
- Choose the compression method based on your requirements. Options include:
- Store: No compression, fastest extraction
- Fastest: Quick compression with minimal size reduction
- Fast: Balanced speed and compression
- Normal: Standard compression ratio
- Good: Higher compression for reduced file size
- Best: Maximum compression, greatest size reduction
3. Enabling Solid Archives:
- Check the “Create solid archive” option to improve compression ratios by merging multiple files into a single data block. This is particularly effective for similar file types.
4. Adjusting Dictionary Size:
- Larger dictionary sizes can lead to better compression ratios but require more memory and processing power. Users can adjust this setting based on their system capabilities and the nature of the files being compressed.
5. Utilizing Fast PPMd or LZMA/LZMA2 Algorithms:
- These advanced algorithms offer superior compression efficiency, especially for text-heavy files. Enabling these can significantly enhance compression ratios.
6. Managing File Attributes:
- Excluding unnecessary attributes like “Read-only” or “Hidden” can streamline the compression process and reduce the archive size.
7. Setting Optimization Preferences:
- WinRAR provides options to optimize archives for specific purposes, such as speeding up extraction or maximizing compression. Users can choose settings that align with their priorities.
Comparison of Compression Settings:
| Compression Setting | Impact on Compression Ratio | Impact on Speed |
|---|---|---|
| **Store** | Minimal | Fastest |
| **Fastest** | Low | Very Fast |
| **Fast** | Moderate | Fast |
| **Normal** | Balanced | Moderate |
| **Good** | High | Slower |
| **Best** | Maximum | Slowest |
Optimization Strategies:
- For Large Files:
Use the “Best” compression method with a larger dictionary size and solid archive setting to achieve maximum size reduction. - For Quick Compress/Extract:
Select the “Fastest” method and avoid solid archives to expedite the process with minimal size gain. - For Frequent Access:
Balance between compression ratio and speed by choosing the “Normal” or “Good” method, ensuring faster access while maintaining reasonable file sizes. - For Specialized Compression:
Utilize specific algorithms like LZMA/LZMA2 for text-heavy or repetitive data to enhance compression efficiency.
Performance Table:
| Scenario | Recommended Settings |
|---|---|
| **Maximum Compression** | Best method, large dictionary, solid archive |
| **Quick Processing** | Fastest or Fast method, no solid archive |
| **Balancing Size and Speed** | Good or Normal method, moderate dictionary |
| **Specialized Compression** | Use specific algorithms like LZMA/LZMA2 |
Example Use Case:
A researcher is preparing to archive a vast collection of academic papers. By configuring WinRAR to use the “Best” compression method with solid archives and a large dictionary size, the researcher maximizes the compression ratio, significantly reducing storage requirements. Additionally, this setup ensures that the archive is efficiently organized, making it easier to share and store the documents.
Additional Tips:
- Regularly Update WinRAR:
Ensure you are using the latest version to benefit from optimizations and new compression algorithms. - Test Different Settings:
Experiment with various settings to find the optimal balance for your specific file types and system capabilities. - Monitor System Performance:
Adjust settings based on your system’s performance. High compression settings may require more RAM and CPU resources.
Configuring WinRAR’s compression settings effectively allows users to tailor the compression process to their specific needs, enhancing both efficiency and performance.
Comparing WinRAR with Other Compression Tools
WinRAR stands out as a powerful tool for file compression and extraction, but how does it compare to other popular compression software? Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each tool can help users make informed decisions based on their specific requirements.
WinRAR vs. 7-Zip: Which One is Better?
WinRAR and 7-Zip are two of the most widely used compression tools available. Both have their unique strengths and cater to different user needs.
Compression Efficiency:
- WinRAR: Known for its proprietary RAR format, which often results in smaller file sizes than traditional ZIP archives. It provides strong compression ratios and is especially efficient when compressing large files, often outperforming 7-Zip in speed but at the cost of compression ratio when using the ZIP format.
- 7-Zip: Utilizes the LZMA and LZMA2 algorithms, offering superior compression ratios, especially for large and text-heavy files. While it may be slower in the compression process compared to WinRAR, 7-Zip excels in delivering maximum compression efficiency, making it ideal for scenarios where reducing file size to the utmost degree is critical.
Feature Comparison:
| Feature | WinRAR | 7-Zip |
|---|---|---|
| **Compression Formats** | RAR, ZIP, TAR, GZ, ISO | 7z, ZIP, TAR, GZ, ISO |
| **Encryption** | AES-256 encryption | AES-256 encryption |
| **Recovery Records** | Yes | No |
| **Self-Extracting Archives** | Yes | Yes |
| **User Interface** | User-friendly, integrated with Windows | Minimalistic, may require familiarity |
| **Licensing** | Shareware | Free and open-source |
Speed:
- WinRAR: Typically faster in both compression and extraction processes due to optimized algorithms and efficient processing.
- 7-Zip: While offering higher compression ratios, it can be slower in the compression process compared to WinRAR, although extraction speed remains competitive.
Pricing:
- WinRAR: Operates on a shareware model with a free trial period of 40 days. Continued use beyond the trial period requires purchasing a license.
- 7-Zip: Completely free and open-source, making it an attractive option for users seeking cost-effective solutions without compromising on performance.
Platform Compatibility:
- WinRAR: Available for Windows, macOS, and Linux, ensuring broad compatibility across different operating systems.
- 7-Zip: Primarily designed for Windows, with unofficial ports available for other platforms, although not as seamlessly integrated as WinRAR.
Conclusion: Choosing between WinRAR and 7-Zip depends on user priorities:
- WinRAR is suited for those who need a balance between speed and efficient compression, along with robust features like recovery records and a user-friendly interface.
- 7-Zip is ideal for users who prioritize maximum compression efficiency without any cost, and who are comfortable with a more minimalistic interface.
WinRAR vs. WinZip: Feature and Performance Comparison
WinRAR and WinZip are two long-standing players in the file compression software market. Both have evolved over the years, each offering a unique set of features tailored to different user needs.
Key Feature Comparison:
| Feature | WinRAR | WinZip |
|---|---|---|
| **Supported Formats** | RAR, ZIP, 7z, TAR, GZ, ISO | ZIP, RAR (extract only), 7z, TAR |
| **Encryption** | AES-256 encryption | AES-256 encryption |
| **Multi-Volume Archives** | Yes | Limited |
| **Recovery Records** | Yes | No |
| **Self-Extracting Archives** | Yes | Yes |
| **Cloud Integration** | Limited | Extensive, integrates with popular cloud services |
| **User Interface** | User-friendly, minimalistic | Modern, feature-rich |
| **Automation Features** | Basic scripting | Advanced automation and sharing tools |
| **Licensing** | Shareware | Proprietary, paid software |
Performance Analysis:
- Compression Efficiency:
- WinRAR: Excels in compressing files into RAR format with high efficiency and speed.
- WinZip: While offering good compression with ZIP format, it may not match WinRAR’s efficiency with RAR-specific compression.
- Security:
- Both WinRAR and WinZip provide AES-256 encryption, ensuring that compressed archives remain secure against unauthorized access.
- Additional Features:
- WinZip: Offers extensive cloud integration, allowing users to save and share archives directly on platforms like Dropbox, Google Drive, and OneDrive.
- WinRAR: Focuses more on robust compression and recovery features rather than cloud integration.
- User Interface:
- WinZip: Features a more visual and modern interface, offering easy access to advanced features and cloud services.
- WinRAR: Maintains a simple, functional interface that focuses on core compression and extraction tasks.
- Pricing:
- WinRAR: Shareware model with a free trial.
- WinZip: Commercially licensed software with various packages and pricing tiers based on features.
Conclusion:
- WinRAR is ideal for users who require powerful compression capabilities and data recovery features. It’s particularly suitable for those who frequently handle large archives and need a reliable tool for compressing and securing files.
- WinZip is better suited for users who need seamless cloud integration and advanced sharing options. Its modern interface and additional automation features make it a preferred choice for those who prioritize ease of use and connectivity with cloud services.
Best Alternatives to WinRAR for File Compression
While WinRAR is a leading tool in file compression, several alternatives offer unique features and benefits that cater to different user preferences and requirements. Here are some of the best alternatives to consider:
1. 7-Zip:
- Overview: A free and open-source compression tool known for its high compression ratios and support for a wide range of formats.
- Features:
- Utilizes LZMA and LZMA2 compression algorithms for efficient data compression.
- Supports the native 7z format, as well as ZIP, RAR (extraction only), TAR, GZ, and more.
- Provides AES-256 encryption for secure file archiving.
- Pros:
- Completely free with no licensing fees.
- Lightweight and highly efficient.
- Superior compression for specific file types, such as text files.
2. WinZip:
- Overview: One of the oldest and most recognized compression tools, offering a multitude of features tailored for both personal and professional use.
- Features:
- Supports various formats, including ZIP, RAR (extraction only), 7z, TAR, GZ, and more.
- Integrates extensively with cloud storage services like Dropbox, Google Drive, and OneDrive.
- Includes advanced features like file splitting, data backup, and direct sharing.
- Pros:
- User-friendly interface with modern design aesthetics.
- Seamless cloud integration enhances sharing and accessibility.
- Offers various automation and sharing tools for enhanced productivity.
3. PeaZip:
- Overview: A free and open-source file archiver that supports over 180 archive types, providing extensive flexibility in file management.
- Features:
- Offers AES-256 encryption to secure archived files.
- Includes conversion tools to switch between different archive formats.
- Compatible with both Windows and Linux, catering to a broad user base.
- Pros:
- Free with no licensing restrictions.
- Versatile with support for an extensive list of archive formats.
- Clean and intuitive user interface, making it easy to navigate.
4. B1 Free Archiver:
- Overview: A free file compression tool that supports numerous archive formats, ideal for users looking for a cost-effective solution.
- Features:
- Offers support for over 20 archive formats including B1, ZIP, RAR, and 7z.
- Provides AES-128 encryption for secure file compression.
- Includes an online converter to transform files between different formats.
- Pros:
- Completely free to use.
- Simple installation and easy-to-use interface.
- Fast compression and extraction speeds.
Comparison Table of Alternatives:
| Alternative Tool | Price | Key Features | Platform Compatibility | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| **7-Zip** | Free | High compression ratios, 7z format | Windows, unofficial ports for other OS | Users seeking open-source and efficient compression |
| **WinZip** | Paid | Cloud integration, modern interface | Windows, Mac | Users needing seamless cloud integration and automation |
| **PeaZip** | Free | Supports 180+ formats, cross-platform | Windows, Linux | Users needing extensive format support and flexibility |
| **B1 Free Archiver** | Free | Supports multiple formats, online conversion | Windows, Mac, Linux | Users seeking a straightforward, free compression tool |
Selecting the Right Tool:
- For Maximum Compression Efficiency:
7-Zip stands out with its superior compression ratios using LZMA algorithms, providing significant size reductions especially for text-heavy files. - For Cloud Integration and Automation:
WinZip excels with its deep integration with cloud services, making it easy to share and access files from popular cloud platforms. - For Extensive Format Support and Flexibility:
PeaZip offers support for an extensive array of archive formats, catering to users who need handling capabilities beyond standard formats. - For a Cost-Effective Solution:
B1 Free Archiver provides a free, easy-to-use alternative for users who require basic compression functionalities without the need for advanced features.
Choosing the best alternative to WinRAR depends on your specific needs from compression efficiency and security to cloud integration and format versatility. Each of these tools offers unique features that can address different aspects of file compression and management, ensuring that you find the perfect fit for your requirements.

Troubleshooting and Common Issues with WinRAR
Even with its robust functionality, users may encounter challenges when using WinRAR. Understanding common issues and their solutions can help ensure a smooth experience with the software.
Fixing Extraction Errors and Corrupt Archives
Extraction errors and corrupt archives can impede access to your files, but WinRAR offers several tools to address these problems effectively.
1. Common Extraction Errors:
- “The archive is corrupted”: Indicates potential data integrity issues or incomplete downloads.
- “Checksum error”: Suggests that the archive’s data does not match its checksum, often due to corruption.
2. Repairing Corrupted Archives:
- Automatic Repair:
- Open WinRAR and select the corrupted archive.
- Navigate to “Tools” > “Repair archive.”
- Choose the archive type (RAR or ZIP) and specify the destination for the repaired file.
- Click “OK” to start the repair process.
- Manual Repair:
- If automatic repair fails, try manually initiating the repair by re-downloading the archive or using another repair tool like PassFab for RAR, which employs methods such as Dictionary Attack to recover the password and repair the archive.
3. Testing Archive Integrity:
- Use the “Test” feature in WinRAR to check the integrity of an archive before extraction.
- Select the archive, click “Tools” > “Test archive,” and wait for WinRAR to verify the file’s integrity.
4. Preventing Future Corruptions:
- Stable Internet Connection:
Ensure a stable connection during downloads to prevent incomplete or corrupted files. - Reliable Storage Media:
Use high-quality storage devices to minimize the risk of data corruption. - Regular Backups:
Maintain backups of essential archives to safeguard against accidental corruption.
5. Additional Tools for Repair:
- Recovery Record:
Use WinRAR’s recovery record feature when creating archives to enhance the ability to repair corrupted files in the future. - Alternate Software:
If WinRAR’s built-in repair feature fails, consider using alternative tools like 7-Zip or specialized recovery software to attempt further data recovery.
Example Use Case:
A user attempts to extract a RAR file containing critical project data but encounters an error message indicating corruption. By utilizing WinRAR’s repair feature, the user initiates the repair process, recovering the majority of the data even if some parts of the archive are damaged. This capability is crucial for salvaging critical information that would otherwise be lost.
Troubleshooting Table:
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| **Extraction Errors** | Corrupt archive file | Use WinRAR’s repair feature |
| **Checksum Errors** | Data corruption | Re-download the archive or repair |
| **Incomplete Downloads** | Interrupted download | Ensure complete download before extraction |
| **File Corruption** | Faulty storage media | Use reliable storage devices |
Preventative Measures:
- Always use official download sources to minimize the risk of corruption.
- Enable recovery records during archive creation to enhance repair capabilities.
- Regularly update WinRAR to benefit from the latest fixes and optimizations.
By following these troubleshooting steps and preventive measures, users can resolve common extraction errors and manage corrupted archives effectively, ensuring continued access to their important files.

Resolving Compatibility Issues with Different File Formats
WinRAR is renowned for its ability to handle various archive formats, but users may still encounter compatibility issues. Understanding how to resolve these challenges ensures smooth file management across different platforms and formats.
1. Unsupported Formats:
- Issue: Some archive formats may not be natively supported by WinRAR, leading to extraction errors or failure to open the archive.
- Solution:
- Update WinRAR: Ensure you are using the latest version of WinRAR, as updates often include support for new formats.
- Use Auxiliary Software: For certain niche formats, consider using specialized extraction tools or converting the archive to a supported format using another utility.
2. Format-Specific Features:
- Issue: Some archive formats have unique features that may not be fully supported or accurately processed by WinRAR.
- Solution:
- Check Configuration Settings: Adjust WinRAR’s settings to better handle specific features of the archive format.
- Compare with Other Tools: Use alternative compression tools like 7-Zip or PeaZip that might handle the format more effectively.
3. Cross-Platform Compatibility:
- Issue: Archives created on different operating systems (e.g., Windows vs. Linux) may encounter compatibility issues when extracted.
- Solution:
- Use Universal Formats: Stick to widely supported formats like ZIP or TAR, which offer better cross-platform compatibility.
- Consistent Settings: Ensure that the same compression settings and algorithms are used when creating and extracting archives across different platforms.
4. Archive Corruption Leading to Compatibility:
- Issue: Corrupted archives may cause compatibility issues, preventing proper extraction.
- Solution:
- Repair the Archive: Utilize WinRAR’s built-in repair tools to fix corrupted archives.
- Alternative Extraction Tools: Try using other tools like 7-Zip or built-in OS utilities to extract the files, as they may handle corrupted data differently.
5. Software Conflicts:
- Issue: Conflicts with other compression software installed on the same system can lead to compatibility issues.
- Solution:
- Disable Conflicting Tools: Temporarily disable or uninstall other compression tools to determine if conflicts are causing the issue.
- Use WinRAR Exclusively: Focus on using WinRAR consistently to manage and extract all archive files, minimizing potential conflicts.
Compatibility Solutions Table:
| Compatibility Issue | Possible Solutions |
|---|---|
| **Unsupported Formats** | Update WinRAR, use auxiliary software |
| **Format-Specific Features** | Adjust settings, use alternative tools |
| **Cross-Platform Issues** | Use universal formats, standardize settings across OS |
| **Archive Corruption** | Repair archives, use alternative extraction tools |
| **Software Conflicts** | Disable conflicting tools, use WinRAR exclusively |
Example Use Case:
A user downloads a TAR.GZ archive created on a Linux system but encounters errors when attempting to extract it on a Windows machine using WinRAR. By updating WinRAR to the latest version and ensuring that all relevant compression algorithms are enabled, the user successfully extracts the archive. Alternatively, switching to 7-Zip for this specific extraction could also resolve the compatibility issue.
Additional Tips:
- Consistently Use Supported Formats:
For best compatibility, prefer formats that are widely supported and avoid obscure or rare archive types. - Stay Updated:
Regularly updating WinRAR ensures access to the latest format support and bug fixes. - Use Multiple Tools:
Sometimes, using a combination of compression tools can help in handling diverse archive formats more effectively.
Resolving compatibility issues with different file formats in WinRAR involves a combination of updating software, choosing the right formats, and sometimes leveraging alternative tools. These strategies ensure that you can manage and access your files seamlessly, regardless of the archive format or operating system.
How to Register and Activate WinRAR
While WinRAR operates on a free trial basis, registering and activating the software ensures uninterrupted access to its full range of features. This section outlines the steps to purchase, register, and activate WinRAR, along with troubleshooting common registration issues.
1. Purchase a License:
- Visit the Official WinRAR Website: Navigate to www.win-rar.com and go to the “Buy” or “Purchase” section.
- Choose a License Type: Select the appropriate license based on your usage needs (individual, business, or volume licenses).
- Complete the Payment: Pay using available payment methods such as credit cards, PayPal, or other local options.
2. Receive the Registration Key:
- After completing the purchase, you will receive an email with a ‘rarkey.rar’ attachment containing your registration details.
- Download the Key File: Save the ‘rarkey.rar’ file to your computer.
3. Install WinRAR:
- Download the latest version of WinRAR from the official website.
- Run the installer and follow the installation prompts to set up WinRAR on your system.
4. Register WinRAR:
- Open WinRAR after installation.
- Right-click on the ‘rarkey.rar’ file and select “Extract Here” or “Extract to rarkey” to unpack the registration key.
- Double-click the extracted ‘runme.exe’ to start the registration process.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the activation.
5. Verify Registration:
- Open WinRAR and go to “Help” > “About WinRAR.”
- Confirm that your registration details appear in the “Registered To” section, indicating successful activation.
Troubleshooting Common Registration Issues:
- Installation Errors:
- Solution:
Run the installer as an administrator by right-clicking the setup file and selecting “Run as administrator.”
- Solution:
- Activation Failure:
- Solution:
Ensure that you have correctly extracted and applied the ‘rarkey.rar’ file. Double-check that the username in the registration key matches the WinRAR installation.
- Solution:
- License Limitations:
- Solution:
Verify that the license type purchased matches your usage requirements. For businesses, ensure a volume license if used on multiple machines.
- Solution:
- Conflicts with Antivirus Software:
- Solution:
Temporarily disable antivirus software during installation and registration, ensuring to re-enable it afterward.
- Solution:
- Lost Registration Key:
- Solution:
Contact WinRAR support with proof of purchase to receive assistance in recovering your registration key.
- Solution:
Example Use Case:
A freelance writer decides to purchase a WinRAR license after the trial period to continue using its advanced features without interruption. Following the purchase, the writer receives the registration key via email. They extract and apply the key using the provided instructions, ensuring that WinRAR remains fully functional for ongoing file compression and management tasks.
Best Practices for Registration:
- Securely Store Registration Details:
Keep a backup of your registration key and purchase confirmation in a secure location to prevent loss or unauthorized access. - Regularly Update WinRAR:
Keep the software updated to the latest version to benefit from security patches and new features. - Review Licensing Terms:
Understand the terms of your purchase, including usage limits and renewal requirements, to ensure compliance and uninterrupted access.
Registering and activating WinRAR unlocks the full potential of the software, providing seamless access to its comprehensive file compression and management features. Following these steps ensures a hassle-free registration process, enabling you to continue leveraging WinRAR for all your file management needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How long is the free trial period for WinRAR?
WinRAR offers a free trial period of 40 days. After the trial, users are encouraged to purchase a license to continue using the software.
2. Can WinRAR handle large files exceeding 4 GB?
Yes, WinRAR can handle large files and archives exceeding 4 GB, making it suitable for storing and managing extensive data sets.
3. Is WinRAR available for Mac and Linux?
Yes, WinRAR is available for Windows, macOS, and Linux, ensuring broad compatibility across different operating systems.
4. Does WinRAR support 7z format?
While primarily using RAR and ZIP formats, WinRAR can also extract 7z archives, though creating 7z files is specific to 7-Zip.
5. Can I use WinRAR without registering it?
WinRAR operates on a free trial basis for 40 days. Continued use beyond the trial period requires purchasing a license and registering the software.
Key Takeaways
Versatile Format Support: WinRAR handles various archive formats, including RAR, ZIP, and more, ensuring flexibility in file management.
Robust Security: Features like AES-256 encryption and password protection safeguard sensitive data effectively.
Advanced Features: Capabilities such as repairing corrupted archives, creating multi-volume archives, and integrating with Windows Explorer enhance usability.
Comparison with Alternatives: While WinRAR offers superior speed and recovery tools, alternatives like 7-Zip provide higher compression ratios and are free.
User-Friendly: The intuitive interface and seamless integration make WinRAR accessible to both novice and advanced users.
Cross-Platform Availability: WinRAR is available on Windows, macOS, and Linux, catering to a wide range of users.
Ongoing Support and Updates: Regular updates ensure that WinRAR remains secure and capable of handling new compression technologies.
Licensing Needs: Users need to purchase and register WinRAR after the trial period to maintain full access to its features.
Conclusion
WinRAR has cemented its status as a premier file compression tool, offering a blend of efficiency, security, and versatility that caters to diverse user needs. Its ability to handle multiple archive formats, coupled with robust encryption and data recovery features, makes it an essential tool for anyone looking to optimize their file management system.
Throughout this guide, we delved into the comprehensive functionalities of WinRAR, from its primary purpose of compressing files to its advanced features like repairing corrupted archives and creating secure, password-protected archives. By comparing WinRAR with other leading tools such as 7-Zip and WinZip, it’s clear that WinRAR holds its own with unique strengths, particularly in speed and data integrity.
Moreover, the step-by-step instructions for downloading, installing, and configuring WinRAR provide users with the knowledge to effectively utilize the software, ensuring a smooth and productive experience. Addressing common issues and troubleshooting techniques further empowers users to overcome potential challenges, maintaining WinRAR as a reliable component of their digital toolkit.
In an increasingly data-driven world, the importance of efficient and secure file management cannot be overstated. WinRAR not only meets these demands but also offers a user-friendly interface that makes complex tasks accessible to all. Whether you’re a professional managing large datasets, a student handling research materials, or an individual looking to secure personal files, WinRAR provides the tools needed to enhance your productivity and protect your data.
Investing time in mastering WinRAR’s features can lead to significant improvements in how you store, share, and manage your files, ultimately making it an invaluable tool in the realm of file compression and extraction.

