Software I love
Tor Browser: The Ultimate Guide to Anonymous and Secure Browsing
Imagine browsing the internet without leaving a trace, free from prying eyes and digital footprints. Sounds like a dream, right? With the Tor Browser, this level of privacy and security is not just possible it’s accessible to everyone. Whether you’re a journalist seeking confidential sources, a whistleblower exposing corruption, or simply someone who values their online privacy, Tor Browser offers a robust solution to safeguard your digital presence.
Introduction
In an era where online privacy is increasingly under threat, the Tor Browser stands out as a beacon of anonymity and security. Developed by the Tor Project, this free and open-source web browser empowers users to navigate the internet without revealing their identity or location. By leveraging the sophisticated Tor network, it ensures that your browsing activities remain hidden from surveillance and tracking, making it an indispensable tool for those who prioritize their digital privacy.
What is Tor Browser?
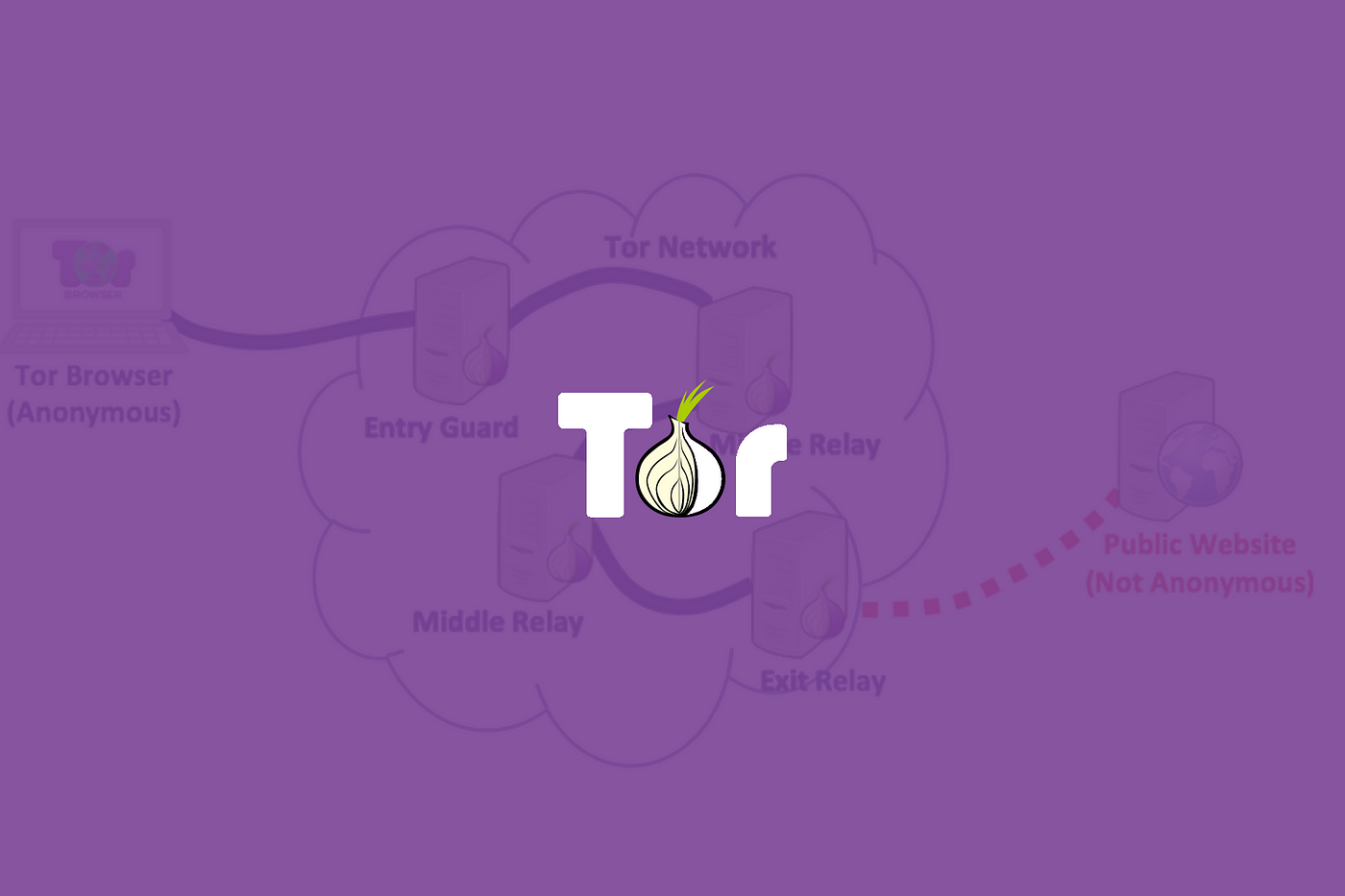
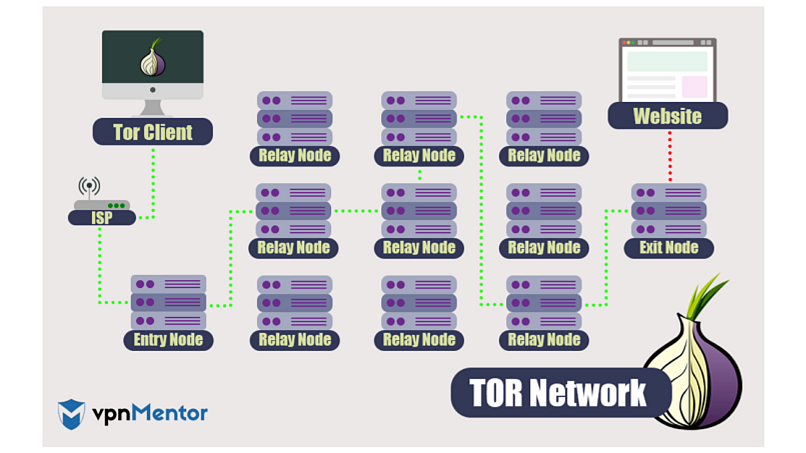
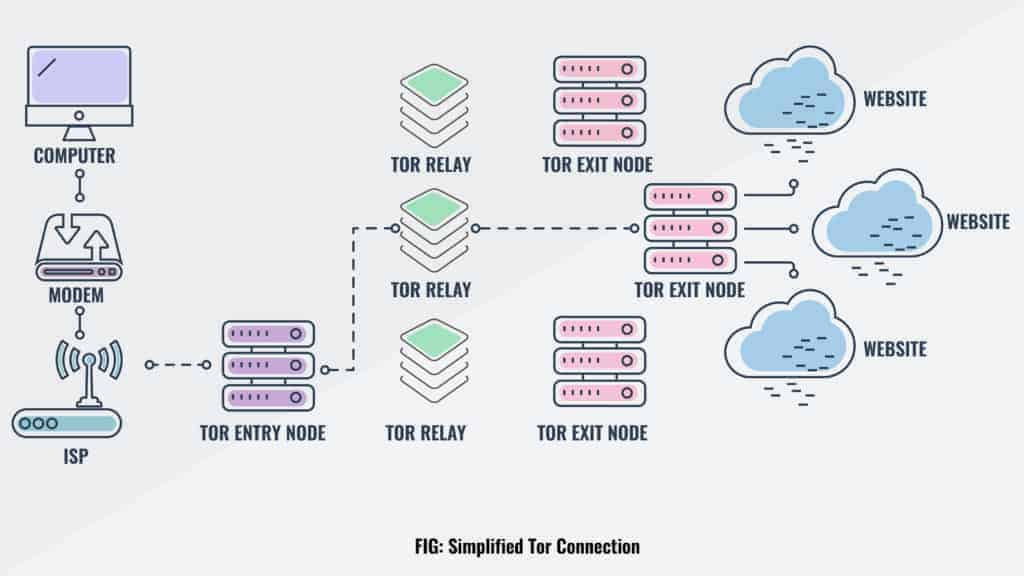
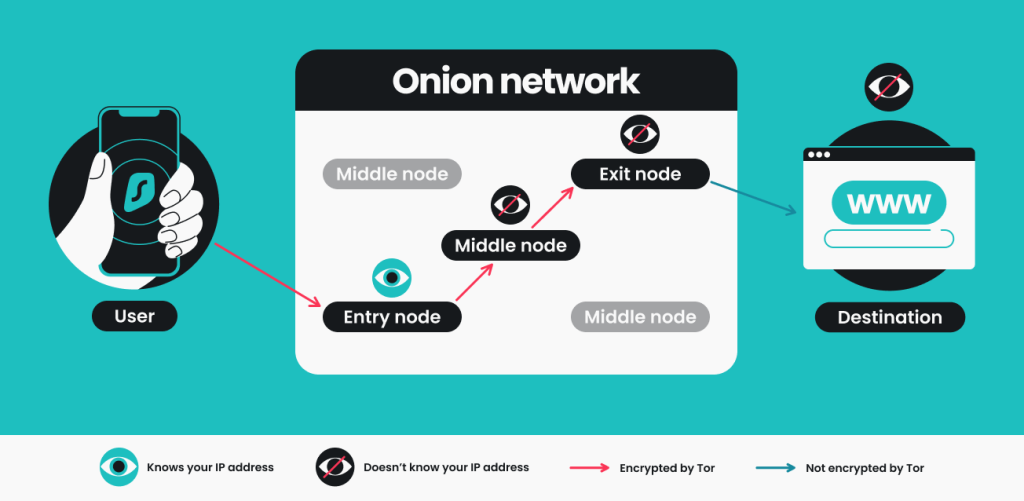
Tor Browser is a specialized web browser designed to facilitate anonymous browsing on the internet. Unlike conventional browsers, Tor routes your internet traffic through a global network of volunteer-operated servers known as relays or nodes. This process, called onion routing, encrypts your data multiple times, making it virtually impossible for anyone to trace your online activities back to you.
Key Features of Tor Browser:
- Onion Routing: Your data is encrypted and sent through multiple relays, obscuring your IP address.
- Access to the Dark Web: Enables access to .onion sites that are not available through standard browsers.
- Enhanced Privacy Settings: Automatically blocks tracking cookies and scripts that can invade your privacy.
- No Trace Browsing: Deletes browsing history and cookies after each session to prevent data leaks.
| Feature | Tor Browser | Traditional Browsers |
|---|---|---|
| Anonymity | High | Low to Moderate |
| Access to Dark Web | Yes | No |
| Built-in Privacy | Extensive (NoScript, HTTPS Everywhere) | Limited (Depends on Extensions) |
| Speed | Slower due to multiple relays | Faster, direct connections |
Tor Browser distinguishes itself by focusing solely on privacy and anonymity, whereas traditional browsers prioritize speed and functionality with optional privacy extensions.
By providing these features, Tor Browser serves as a powerful tool for users who need to protect their identity online, whether for personal privacy or professional reasons.
How Tor Browser Works to Protect Privacy
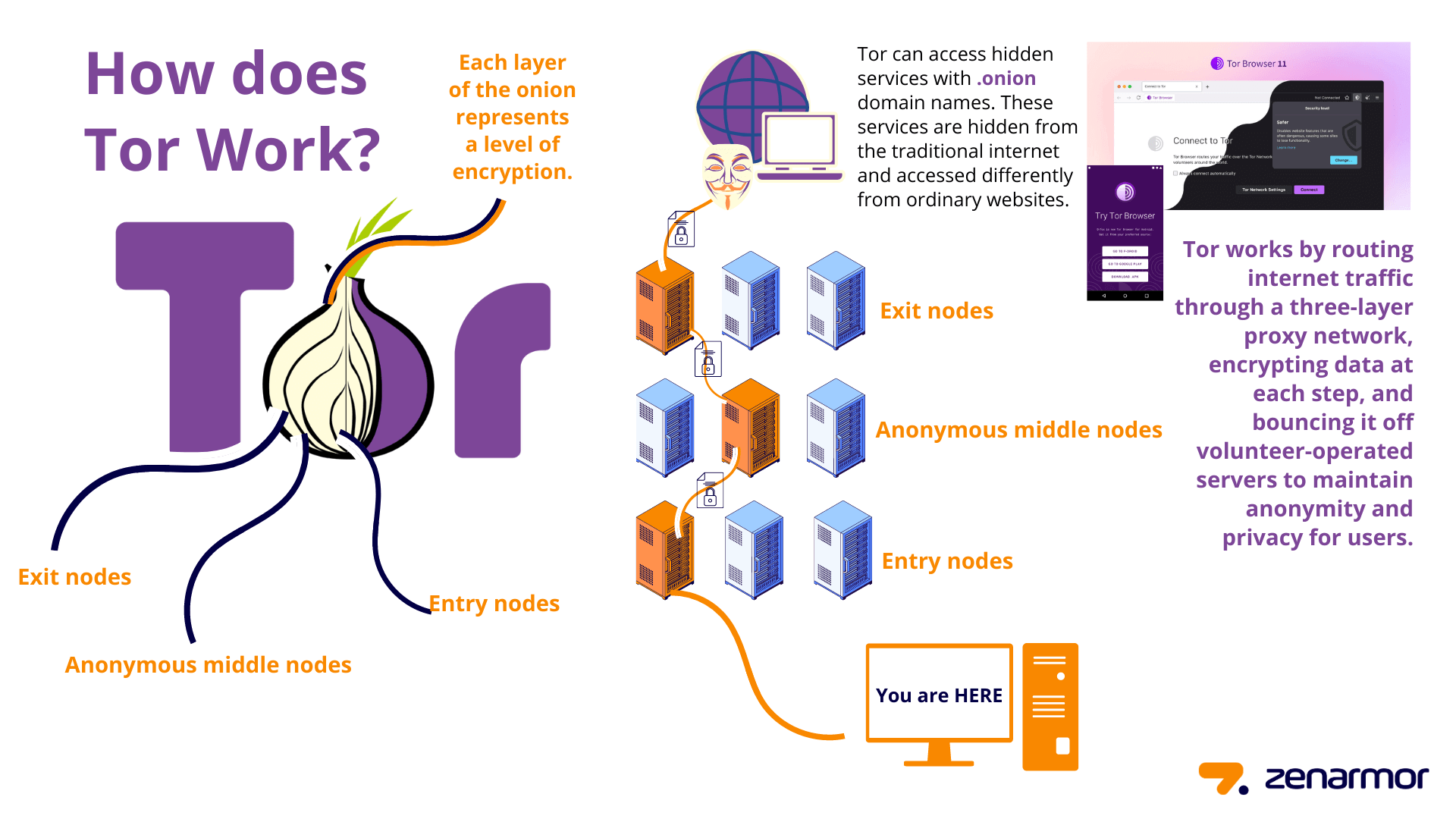
Tor Browser employs a unique method known as onion routing to ensure user anonymity and data security. This method involves multiple layers of encryption that make tracing the origin of internet traffic extremely difficult.
How Onion Routing Works:
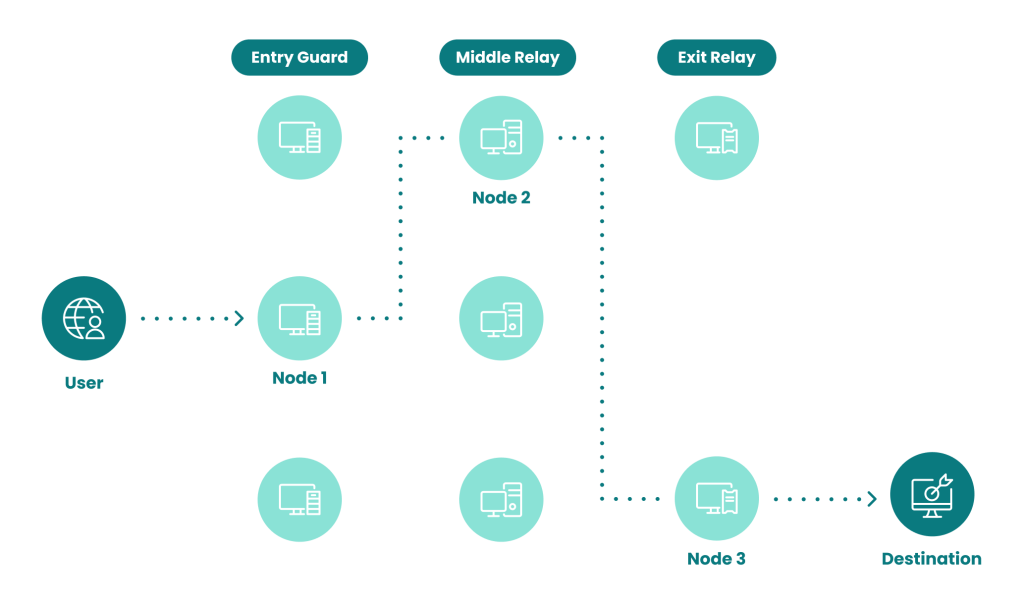
- Entry Node: The user’s data is first encrypted and sent to an entry node, which knows the user’s IP address but not the final destination.
- Middle Nodes: The data is then passed through several middle nodes, each decrypting a layer of encryption, making it impossible to trace the original source.
- Exit Node: The final node decrypts the last layer and sends the data to the desired internet destination, unaware of the user’s IP address.
Advantages of Tor’s Privacy Protection:
- Distributed Network: Eliminates single points of failure, reducing the risk of centralized surveillance.
- Layered Encryption: Ensures that even if one relay is compromised, the data remains secure.
- No Central Logging: The decentralized nature of Tor means there’s no central repository of user data that can be targeted.
| Privacy Aspect | Tor Browser | Standard Browsers |
|---|---|---|
| IP Address Masking | Yes | Limited (Requires VPN) |
| Data Encryption | Multiple layers through relay nodes | Single layer (HTTPS) |
| Surveillance Resistance | High, distributed network | Low, centralized servers |
| Traffic Analysis Resistance | Strong, multiple encryption layers | Weak, easier to trace |
The multilayered approach of Tor provides superior protection against traffic analysis and IP tracking compared to standard browsers, which rely on simpler encryption methods.
Moreover, Tor Browser includes additional privacy-enhancing features, such as blocking third-party trackers and preventing fingerprinting techniques that websites use to identify and track users. These combined measures make Tor Browser an essential tool for maintaining privacy in an environment where online surveillance is becoming increasingly pervasive.
Why Use Tor for Anonymous Browsing?
Choosing Tor Browser for anonymous browsing offers numerous benefits, particularly for those who require a high level of privacy and security.
Benefits of Using Tor:
- Anonymity: Masks your IP address, making it difficult for websites and third parties to track your location and activities.
- Circumventing Censorship: Allows access to blocked or restricted websites by bypassing geographic and governmental restrictions.
- Protection from Tracking: Prevents advertisers and data collectors from building profiles based on your browsing habits.
- Secure Communication: Guards against eavesdropping by encrypting your internet traffic multiple times.
Who Can Benefit from Tor:
- Journalists: Protect sources and confidential communications.
- Activists: Operate safely in oppressive regimes.
- Everyday Users: Maintain personal privacy and prevent tracking by third parties.
| Use Case | Tor Browser | VPNs | Standard Browsers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Journalism | High anonymity, secure communication | Varies by provider, some logs may exist | Low anonymity |
| Activism | Strong resistance to censorship | Limited by provider’s jurisdiction | Easily censored by governments |
| Everyday Privacy | Comprehensive tracking prevention | Protects IP, but provider can log data | Tracking enabled by default |
| Access to Dark Web | Direct access to .onion sites | Limited or no access | No access |
While VPNs offer benefits like IP masking and data encryption, Tor provides a higher level of anonymity without relying on a single service provider, reducing the risk of data logging and surveillance.
Emphasizing these advantages, Tor Browser is not just another web browser it’s a gateway to a more private and secure internet experience. Whether you’re safeguarding your personal information or accessing information in restrictive environments, Tor offers the tools necessary to maintain your digital freedom.
How to Download and Install Tor Browser
Getting started with Tor Browser is straightforward. Follow these steps to ensure a secure and seamless installation process.
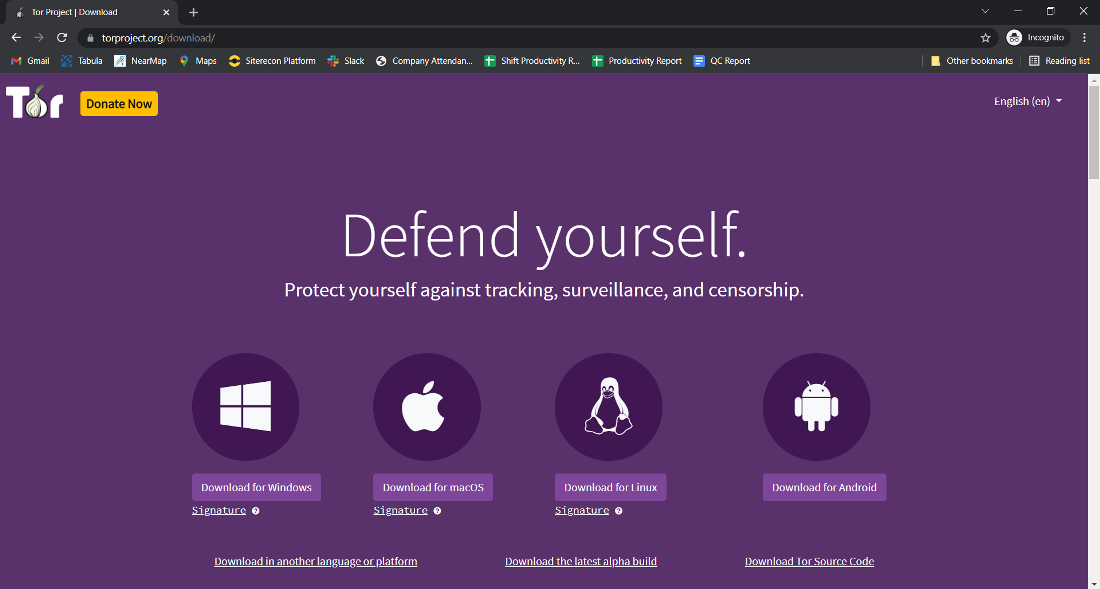
Where to Download Tor Browser Safely
To ensure that you download the legitimate version of Tor Browser without any malicious software, it’s crucial to obtain it from a trusted source.
Steps to Download Safely:
- Official Website: Always download Tor Browser from the official Tor Project website. This guarantees that you receive the latest, unaltered version.
- Verify Downloads: After downloading, verify the file’s signature using the instructions provided on the website. This step ensures the integrity and authenticity of the software.
- Avoid Third-Party Sources: Refrain from downloading Tor from third-party sites or unofficial mirrors, as these can be compromised.
Advantages of Official Downloads:
- Security: Reduced risk of downloading tampered or infected files.
- Updates: Immediate access to the latest security patches and features.
- Support: Guaranteed compatibility and support from the Tor Project.
| Source | Trust Level | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Official Tor Project | High | Secure, up-to-date, supported | May be blocked in restrictive regions |
| Third-Party Sites | Low to Moderate | Sometimes faster or alternative formats | Risk of malware, tampering |
| Mirror Sites | Moderate | Backup option if official site is down | Potential for outdated versions |
Downloading from the official Tor Project website ensures maximum security and access to the latest updates, making it the most reliable source.
Additionally, if you encounter restrictions accessing the official site, the Tor Project provides alternative methods such as using GetTor, which allows downloading via email or Telegram, ensuring accessibility regardless of your location’s internet policies.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide for Windows, Mac, and Linux
Installing Tor Browser is a simple process that varies slightly depending on your operating system. Follow the instructions below tailored to your specific platform.
Windows Installation:
- Download the Installer:
- Visit the Tor Project download page and download the Windows ‘.exe’ file.
- Run the Installer:
- Locate the downloaded file and double-click the executable to start the installation.
- Security Warning:
- If prompted, confirm that you trust the source and proceed by clicking “Run.”
- Choose Language:
- Select your preferred language and click “OK.”
- Installation Path:
- Choose the destination folder or accept the default path, then click “Install.”
- Launch Tor Browser:
- Once installation is complete, click “Finish” to open Tor Browser.
Mac Installation:
- Download the ‘.dmg’ File:
- Access the Tor Project download page and download the macOS ‘.dmg’ file.
- Open the Installer:
- Double-click the downloaded file to mount the Tor Browser disk image.
- Move to Applications:
- Drag the Tor Browser icon into the Applications folder as instructed.
- Security Approval:
- If prompted by macOS security settings, approve the installation in System Preferences.
- Launch Tor Browser:
- Navigate to the Applications folder and open Tor Browser.
Linux Installation:
- Download the ‘.tar.xz’ File:
- Go to the Tor Project download page and download the Linux ‘.tar.xz’ archive.
- Extract the Archive:
- Open a terminal and run:tar -xf tor-browser-linux64-version.tar.xz
- Navigate to the Directory:
- Change to the extracted folder:cd tor-browser_en-US
- Run the Installation Script:
- Execute the script to start Tor Browser:./start-tor-browser.desktop
- Follow On-Screen Instructions:
- Complete the setup by following the prompts in the Tor Browser.
System Requirements for Running Tor Browser
Before installing Tor Browser, ensure that your system meets the necessary requirements to run it smoothly.
Minimum System Requirements:
- Operating Systems:
- Windows 7 or later
- macOS 10.10 (Yosemite) or later
- Linux distributions supporting 32-bit or 64-bit architectures
- Hardware:
- Modern processor
- At least 2 GB of RAM for optimal performance
- Internet Connection:
- Stable broadband connection
- Recommended speed: 1 Mbps or higher for better performance
Additional Recommendations:
- Antivirus Software:
- Ensure that your antivirus or firewall does not block Tor Browser.
- Permissions:
- Administrative rights may be required for installation on some operating systems.
| Operating System | Supported Versions | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Windows | 7, 8, 10, 11 | Ensure compatibility with system updates |
| macOS | 10.10 and later | Regular updates recommended |
| Linux | Various distributions | Verify dependencies are met |
Meeting these requirements ensures that Tor Browser operates efficiently, providing a seamless and secure browsing experience.
For detailed and up-to-date information, refer to the official Tor Project documentation which provides comprehensive guidance on system compatibility and troubleshooting.
Features and Benefits of Tor Browser
Tor Browser is packed with features that enhance privacy and security, making it a preferred choice for anonymous internet browsing. These features not only protect your identity but also provide a safer online experience.
Anonymous Browsing with Onion Routing
At the heart of Tor Browser lies onion routing, a method that ensures your online activities remain concealed.
How Onion Routing Enhances Anonymity:
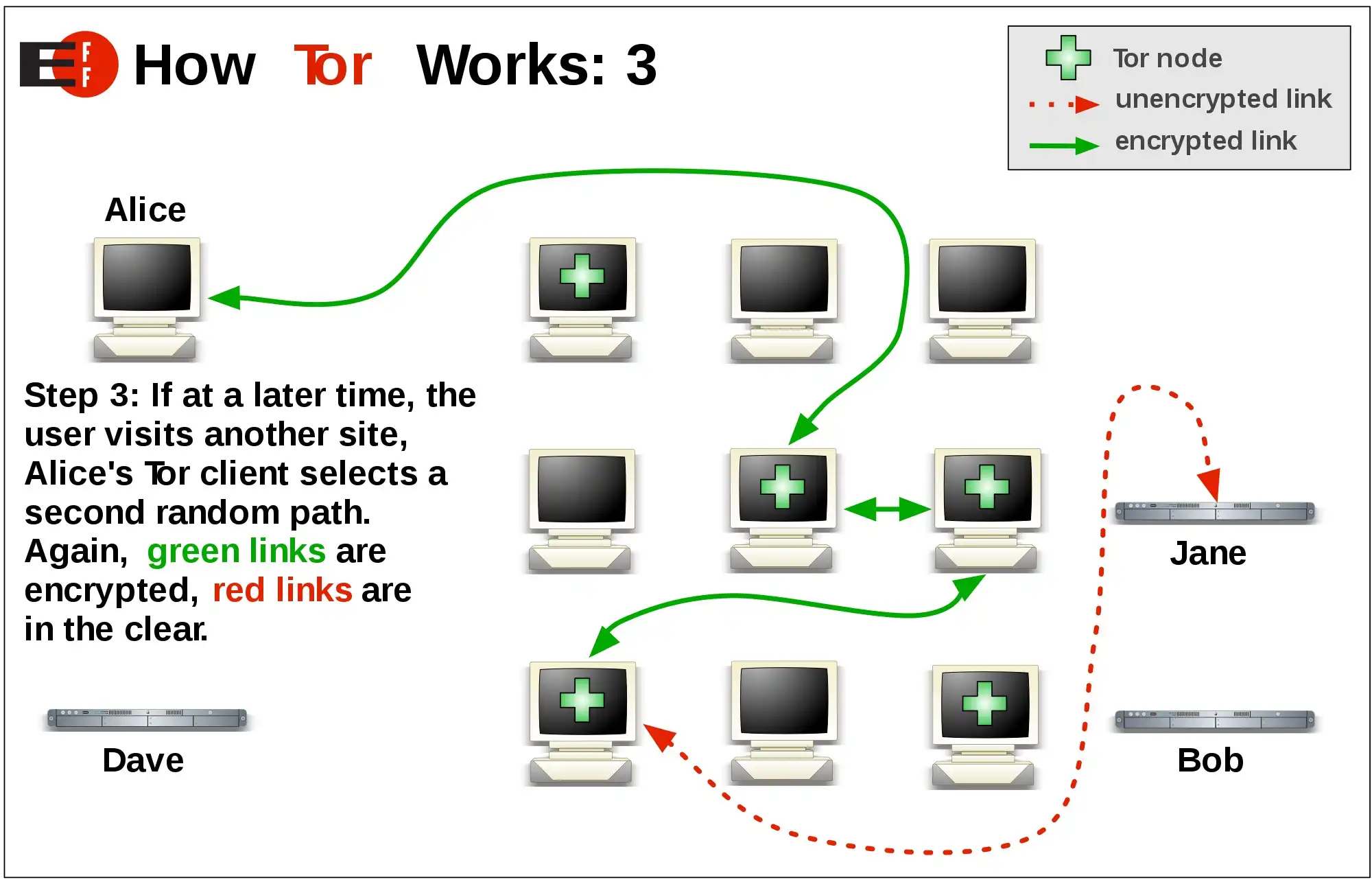
- Multiple Encryption Layers: Data is encrypted in layers, similar to an onion, ensuring each relay removes only one layer, keeping the original source hidden.
- Randomized Pathways: Each connection follows a random path through different nodes, making it difficult to predict or trace the route.
- Distributed Network: With thousands of volunteer-operated relays worldwide, the decentralized nature prevents single-point tracking.
Advantages:
- High Anonymity: Difficult for adversaries to trace activities back to the user.
- Resistance to Eavesdropping: Protects against network surveillance and traffic analysis.
- Dynamic Circuit Paths: Regularly changes paths to enhance security and anonymity.
| Aspect | Onion Routing with Tor | Standard Routing |
|---|---|---|
| Data Encryption | Multiple layers | Single layer (HTTPS) |
| Pathway Randomization | High | Low |
| Network Density | Decentralized, many relays | Centralized servers |
| Tracking Resistance | Excellent | Limited |
Onion routing provides a robust framework for maintaining anonymity, surpassing traditional routing methods in privacy protection.
In practice, when you use Tor Browser, your data travels through a series of relays entry, middle, and exit each stripping away a layer of encryption. This process ensures that no single relay knows both the source and destination of the data, effectively masking your identity and location.
Bypassing Censorship and Accessing Restricted Content
In many parts of the world, governments and organizations impose strict internet censorship, limiting access to information and communication platforms. Tor Browser provides a powerful solution to bypass these restrictions.
Capabilities of Tor in Bypassing Censorship:
- Geo-Independent Access: By routing traffic through international relays, users can access content restricted in their region.
- Circumventing Firewalls: Tor effectively bypasses firewalls and content filters imposed by ISPs or governmental bodies.
- Access to Blocked Services: Enables access to social media platforms, news websites, and other blocked services without detection.
Benefits:
- Freedom of Information: Unrestricted access to global information allows users to stay informed and connected.
- Secure Communication: Facilitates safe communication for activists and journalists in oppressive regimes.
- Anonymized Access: Protects users from retaliatory measures when accessing sensitive or controversial content.
| Censorship Aspect | Tor Browser | VPNs | Proxy Servers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Firewall Circumvention | Highly Effective | Effective, depends on VPN strength | Limited effectiveness |
| Access to Blocked Platforms | Direct access to .onion sites | May require specific server locations | Often blocked or unreliable |
| Anonymity Level | Very High | High, but dependent on VPN provider | Low to Moderate |
Tor Browser offers unparalleled capabilities in bypassing censorship compared to VPNs and proxy servers, making it a vital tool in restricted environments.
Moreover, Tor’s ability to access the dark web expands the range of content beyond what is available on the clearnet. While the dark web is often associated with illicit activities, it also hosts legitimate services like secure forums, whistleblowing platforms, and privacy-focused communications that are essential for users seeking unmonitored online spaces.

Enhanced Privacy Protection with No Tracking
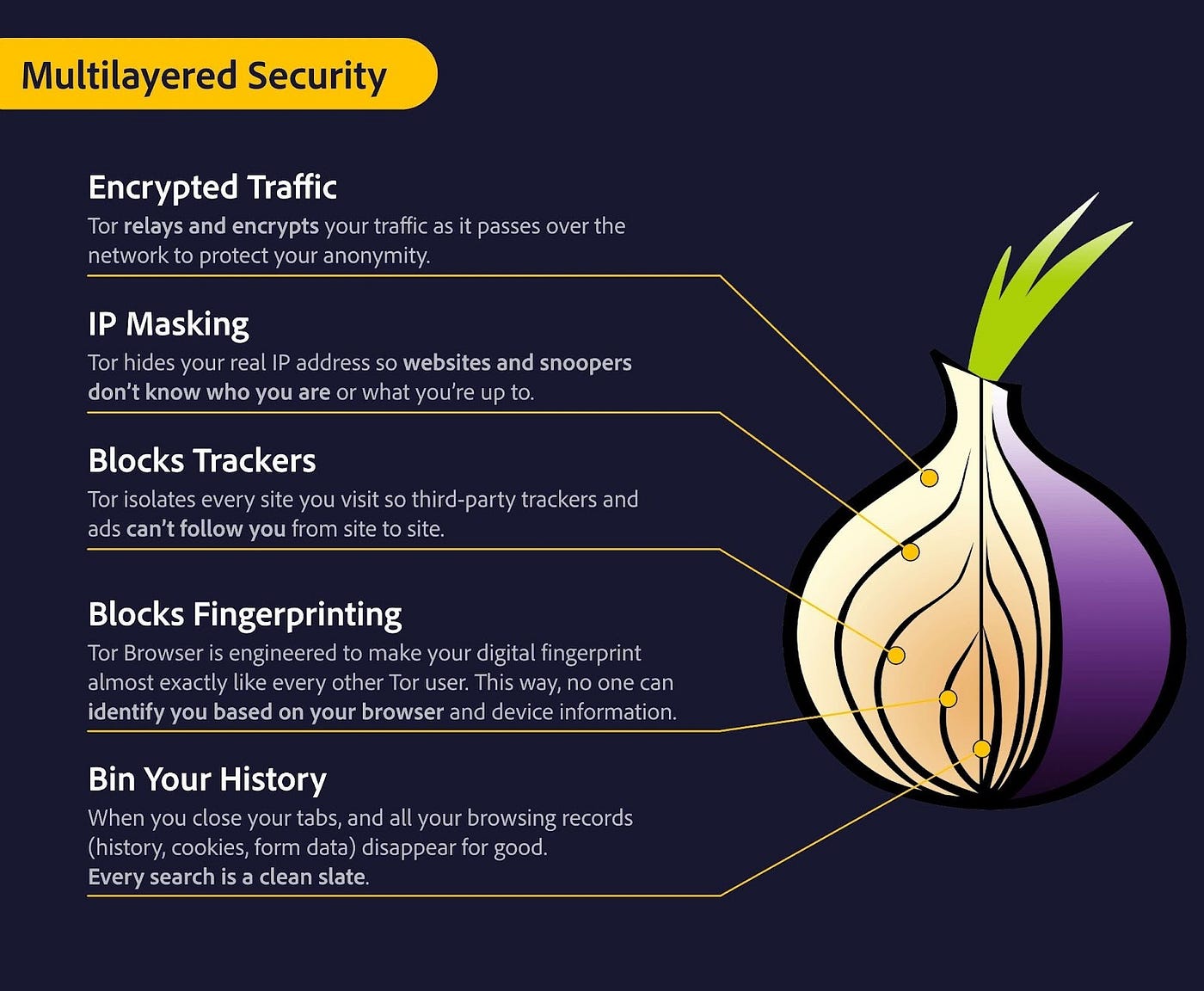
Tor Browser goes beyond mere anonymity by implementing comprehensive privacy protection measures that prevent tracking and profiling.
Privacy Features:
- No Tracking Cookies: Automatically blocks third-party cookies and trackers, preventing websites from tracking your browsing habits.
- Fingerprint Resistance: Minimizes browser fingerprinting techniques that identify unique user configurations and behaviors.
- Private Browsing Mode: Clears all browsing data, including history, cookies, and cache, after each session to ensure no residual data remains.
Benefits:
- Reduced Data Collection: Limits the amount of personal data collected by advertisers and data brokers.
- Enhanced Security: Protects against malicious scripts and trackers that can exploit user data.
- Consistent Privacy: Maintains privacy across multiple browsing sessions without additional configurations.
| Privacy Protection Feature | Tor Browser | Standard Browsers with Extensions | Features Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cookie Blocking | Automatic and comprehensive | Requires manual setup | Tor offers out-of-the-box protection |
| Fingerprint Resistance | Built-in protections | Limited or reliant on add-ons | Tor provides stronger resistance |
| Data Clearing | Automatic after each session | Manual or periodic clearing | Tor automates the process |
The integrated privacy features of Tor Browser ensure that users experience a secure and private browsing session without the need for additional tools or extensions.
Furthermore, Tor’s commitment to privacy is reflected in its default configurations that prioritize security over convenience. By disabling plugins, limiting script execution, and enforcing strict privacy settings, Tor minimizes the avenues through which data can be collected or leaked, offering a sanctuary for those who demand uncompromised privacy.
Automatic Encryption for Online Communications
One of the standout features of Tor Browser is its ability to automatically encrypt your internet communications, ensuring that your data remains secure and private.
How Automatic Encryption Works:
- End-to-End Encryption: Data is encrypted from your device all the way to the exit node, preventing interception by third parties.
- Layered Security: Each relay in the Tor network decrypts a single layer of encryption, making it impossible for any single point to access the complete data.
- Seamless Integration: Users do not need to manually configure encryption settings, as Tor Browser handles encryption seamlessly in the background.
Advantages of Automatic Encryption:
- Data Integrity: Protects against data tampering and eavesdropping.
- User Convenience: Eliminates the need for manual encryption setup, making secure browsing accessible to everyone.
- Enhanced Security: Provides robust protection against cyber threats such as man-in-the-middle attacks and surveillance.
| Encryption Aspect | Tor Browser | Standard Browsers with HTTPS | Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Encryption | Multiple layers through Tor nodes | Single layer with HTTPS | Tor offers more comprehensive encryption |
| User Configuration Required | No | No | Both are user-friendly |
| Resistance to Interception | High | Moderate to High | Tor provides higher resistance |
Automatic encryption ensures that all your online communications are secured without any additional effort on your part.
Moreover, Tor Browser includes built-in tools like HTTPS Everywhere, which forces secure connections to websites whenever possible. This integration ensures that your data remains encrypted even when connecting to sites that support HTTPS, adding an extra layer of security to your browsing activities.
How to Use Tor Browser Effectively
Maximizing the benefits of Tor Browser requires understanding how to configure and use its features properly. This section provides practical advice to help you navigate the internet securely and anonymously.
Setting Up and Configuring Tor for Maximum Privacy
To ensure that you achieve the highest level of privacy while using Tor Browser, proper setup and configuration are essential.
Steps to Optimize Privacy:
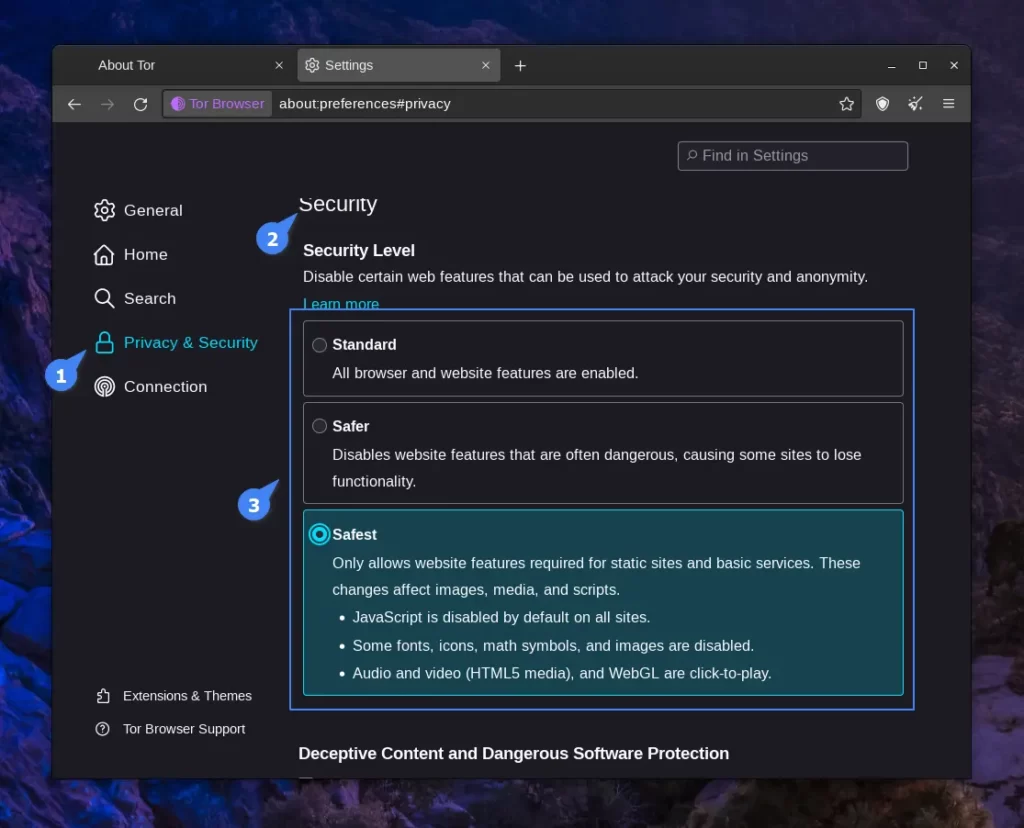
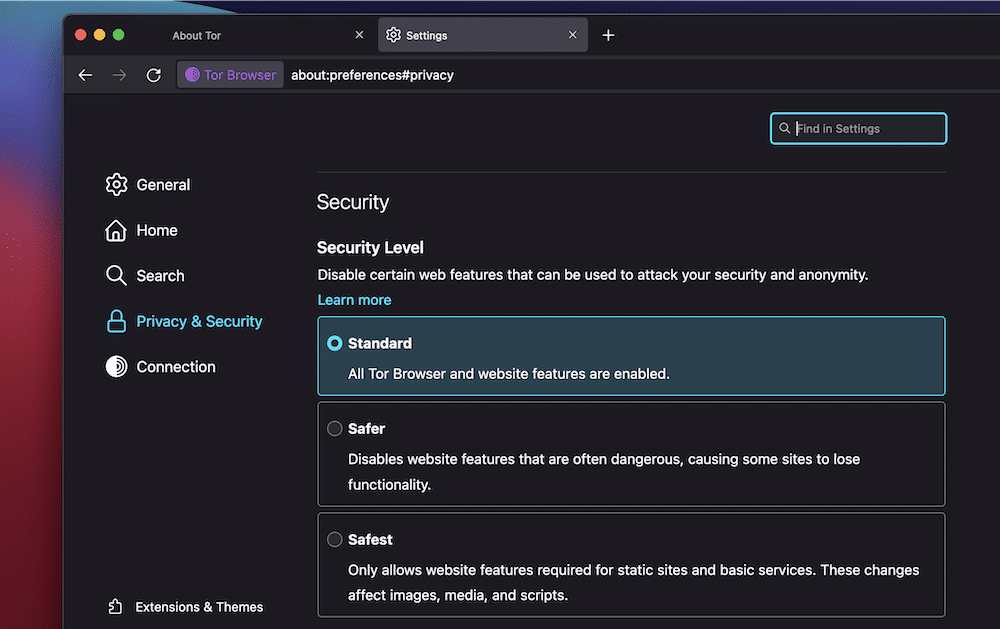
- Adjust Security Settings:
- Click on the Shield icon next to the URL bar.
- Select the desired security level: Standard, Safer, or Safest. Higher levels disable JavaScript and other potentially risky features.
- Use Bridges:
- If Tor is blocked in your region, use bridges to access the network covertly.
- Configure bridges in the Tor Browser settings under the “Tor Network Settings” section.
- Disable Scripts:
- Use the built-in NoScript extension to control which scripts run on the websites you visit.
- Consider disabling JavaScript entirely for sites that do not require it.
- Enable HTTPS Everywhere:
- Ensure that HTTPS Everywhere is activated to force secure connections to websites whenever possible.
- Regularly Update Tor Browser:
- Keep Tor Browser updated to benefit from the latest security patches and features.
| Configuration Step | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Adjust Security Levels | Set to Safer or Safest for higher security | Reduces risk of browser-based attacks |
| Use Bridges | Access Tor discreetly in restricted areas | Bypasses network restrictions |
| Disable Scripts | Control or block scripts on websites | Prevents malicious code execution |
| Enable HTTPS Everywhere | Ensure encrypted connections to websites | Enhances data security |
| Regular Updates | Keep Tor Browser current with security patches | Protects against vulnerabilities |
Configuring these settings ensures that you are leveraging Tor Browser’s full potential for maximum privacy and security.
Additionally, consider using a separate user profile in Tor Browser to compartmentalize different aspects of your online activities. This practice helps prevent cross-contamination of data and maintains a clean separation between various browsing sessions, enhancing overall anonymity.
How to Browse the Dark Web Safely
The dark web, accessible exclusively through Tor, offers a vast array of resources, but it also comes with inherent risks. Here’s how to navigate it safely:
Safety Guidelines:
- Stick to Reputable Sites:
- Use verified directories like the Hidden Wiki to find trustworthy .onion sites.
- Avoid clicking on unknown links that could lead to malicious content.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Information:
- Never disclose your real identity, location, or sensitive data.
- Use anonymous usernames and secure communication methods.
- Be Cautious with Downloads:
- Only download files from trusted sources to avoid malware.
- Scan all downloads with updated antivirus software before opening.
- Use Additional Security Tools:
- Consider using encrypted messaging services for communication.
- Utilize PGP encryption for sensitive emails and data.
- Regularly Update Security Settings:
- Keep Tor Browser’s security settings at the highest level to minimize vulnerabilities.
- Disable unnecessary features that could compromise your anonymity.
| Safety Practice | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Reputable Sites | Use trusted directories for .onion links | Reduces exposure to malicious sites |
| Anonymity | Avoid sharing personal details | Protects your identity |
| Secure Downloads | Download only from trusted sources | Prevents malware infections |
| Additional Security Tools | Use encrypted communication methods | Enhances data security |
| Regular Security Updates | Maintain high security settings | Minimizes vulnerabilities |
Adhering to these safety practices allows you to explore the dark web while minimizing risks and protecting your anonymity.
Furthermore, being aware of the types of content and activities prevalent on the dark web can help you make informed decisions about where to navigate. Understanding the distinction between legal and illegal activities is crucial to maintaining ethical and safe browsing habits.
Customizing Security and Privacy Settings
Tor Browser offers various customization options that allow users to tailor their security and privacy levels according to their specific needs.
Customization Options:
- Security Levels:
- Access the Security Settings via the Shield icon.
- Choose between Standard, Safer, and Safest levels to control JavaScript, images, and other web elements.
- NoScript Settings:
- Configure NoScript to allow or block scripts on specific websites.
- Set default permissions to restrict potentially harmful scripts.
- Privacy Preferences:
- Adjust settings to block third-party trackers and cookies.
- Enable “New Identity” to reset your browsing session and clear all data.
- Appearance and Functionality:
- Customize the browser’s appearance, such as themes and fonts, to suit your preferences without compromising security.
- Disable unnecessary plugins and extensions that may interfere with privacy settings.
- Network Settings:
- Configure bridges and pluggable transports to enhance connectivity in restricted environments.
- Adjust proxy settings if required by your network configuration.
Benefits of Customization:
- Enhanced Security: Fine-tuning settings to block specific web elements reduces the attack surface.
- Improved Privacy: Custom configurations prevent different tracking methods from compromising your anonymity.
- User Experience: Balancing security with usability ensures a smoother browsing experience without significant performance drawbacks.
| Customization Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Security Levels | Adjust protection tiers | Tailored security vs usability |
| NoScript Settings | Control script execution | Prevents malicious script attacks |
| Privacy Preferences | Manage tracking and cookie settings | Enhances user privacy |
| Appearance Customization | Personalize browser look and feel | Improves user experience |
| Network Settings | Configure connectivity options | Ensures access in restricted areas |
By customizing these settings, users can optimize their Tor Browser for maximum privacy and security without sacrificing usability.
Additionally, regularly reviewing and updating these settings is essential to adapt to new security threats and maintain robust protection against evolving surveillance techniques.

Comparing Tor Browser with Other Privacy Browsers
While Tor Browser is a standout choice for privacy and anonymity, it’s important to understand how it stacks up against other privacy-focused browsers. This comparison highlights the unique strengths and potential limitations of Tor in relation to its competitors.
Tor Browser vs. VPNs: Which is Better for Anonymity?
When it comes to online anonymity, both Tor Browser and Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) offer distinct benefits. Understanding their differences is crucial for choosing the right tool for your privacy needs.
Tor Browser:
- Anonymity: Provides high levels of anonymity by routing traffic through multiple relays, making it difficult to trace.
- Decentralization: Operates on a decentralized network of volunteer-run servers, reducing reliance on any single entity.
- Access to Dark Web: Enables access to .onion sites, expanding browsing capabilities beyond the clearnet.
- Speed: Slower browsing speeds due to multi-hop routing and encryption processes.
VPNs:
- Anonymity: Offers moderate anonymity by masking your IP address, but the VPN provider can potentially log your activities.
- Centralization: Relies on centralized servers managed by VPN providers, which can be a single point of vulnerability.
- Access to Dark Web: Does not natively support access to the dark web; additional configurations or tools may be required.
- Speed: Generally faster browsing speeds compared to Tor, as traffic is routed through fewer servers.
| Feature | Tor Browser | VPNs |
|---|---|---|
| Anonymity | High | Moderate |
| Network Type | Decentralized, volunteer-operated relays | Centralized, provider-managed servers |
| Dark Web Access | Direct access to .onion sites | Limited, requires additional setup |
| Speed | Slower due to multiple relays | Faster, fewer hops |
| Logging Policies | No central logging | Depends on provider, some log data |
Tor Browser excels in anonymity through its decentralized network and multi-layered encryption, whereas VPNs offer faster speeds with varying levels of privacy depending on the provider’s policies.
Choosing Between Tor and VPNs:
- Use Tor Browser if:
- You prioritize maximum anonymity and privacy.
- You need access to the dark web.
- You can tolerate slower browsing speeds.
- Use a VPN if:
- You require faster internet speeds for streaming or downloading.
- You need to mask your IP address from websites.
- You trust the VPN provider’s privacy policies and logging practices.
By evaluating your specific privacy needs and usage scenarios, you can determine which tool Tor Browser or a VPN best aligns with your requirements for online anonymity and security.
Tor Browser vs. Brave: Security and Performance Comparison
Brave is another privacy-focused browser that competes with Tor Browser by offering built-in privacy features. Here’s how they compare in terms of security and performance.
Tor Browser:
- Security Features:
- Onion routing for enhanced anonymity.
- Integrated NoScript and HTTPS Everywhere.
- Strict privacy settings by default.
- Performance:
- Slower due to traffic passing through multiple relays.
- Suitable for tasks where speed is less critical than privacy.
Brave Browser:
- Security Features:
- Built-in ad and tracker blocking.
- Shields that block third-party cookies, scripts, and fingerprinting.
- Optional Tor integration for specific tabs, providing limited anonymity.
- Performance:
- Faster browsing speeds compared to Tor Browser.
- Optimized for everyday use with minimal performance trade-offs.
| Aspect | Tor Browser | Brave Browser |
|---|---|---|
| Anonymity | High (onion routing) | Moderate (optional Tor tabs) |
| Built-in Privacy | Extensive (NoScript, HTTPS Everywhere) | Strong (ad and tracker blocking) |
| Speed | Slower due to multiple relays | Faster, optimized for regular use |
| Dark Web Access | Direct access to .onion sites | Limited, requires separate configuration |
| User Experience | Focused on privacy, less on speed | Balanced between privacy and performance |
While both browsers prioritize privacy, Tor Browser offers superior anonymity through its unique routing system, whereas Brave provides a more balanced approach with enhanced security features and better performance for everyday browsing.
Key Considerations:
- Privacy Needs:
- If absolute anonymity is essential, Tor Browser is the better choice.
- For enhanced privacy without significant speed penalties, Brave is suitable.
- Usage Patterns:
- Use Tor Browser for sensitive tasks requiring high security.
- Use Brave for regular browsing with built-in privacy protections.
By understanding these differences, users can choose the browser that best fits their privacy needs and usage preferences.

Tor Browser vs. Firefox: Features and Privacy Benefits
Mozilla Firefox is a widely-used browser known for its customization and strong privacy features. Comparing it to Tor Browser highlights the distinct approaches each takes towards user privacy.
Tor Browser:
- Privacy Features:
- Onion routing for anonymity.
- Automatic blocking of third-party trackers and cookies.
- Built-in NoScript and HTTPS Everywhere for enhanced security.
- Customization:
- Limited to maintain security and anonymity.
- Focuses on providing a secure default configuration rather than extensive user customization.
Firefox:
- Privacy Features:
- Enhanced Tracking Protection to block trackers and cookies.
- Privacy-focused extensions available via add-ons.
- Customizable privacy and security settings.
- Customization:
- Extensive customization options through themes and extensions.
- Users can tailor the browser to their specific privacy needs, balancing functionality and security.
| Feature | Tor Browser | Firefox |
|---|---|---|
| Anonymity | High (onion routing) | Moderate (Enhanced Tracking Protection) |
| Privacy Tools | NoScript, HTTPS Everywhere | Built-in tracking protection, privacy extensions |
| Customization | Limited to preserve security | Highly customizable with extensions and themes |
| Dark Web Access | Direct access to .onion sites | No native support for dark web access |
| Performance | Slower due to multiple relay hops | Faster, optimized for general use |
Tor Browser offers superior anonymity through its network structure, while Firefox provides robust privacy features with greater customization options for users.
Privacy and Usability:
- Tor Browser: Best for users who need strong anonymity and are willing to accept slower performance for enhanced privacy.
- Firefox: Ideal for users seeking a balance between privacy, customization, and performance, with the flexibility to add specific privacy enhancements as needed.
By leveraging Firefox’s customizable privacy settings, users can achieve a high level of protection, albeit without the comprehensive anonymity that Tor Browser provides. This makes Firefox suitable for everyday users who desire strong privacy without sacrificing browsing speed.
Limitations and Risks of Using Tor Browser
While Tor Browser offers significant privacy and security advantages, it’s important to be aware of its limitations and associated risks to use it effectively and safely.

Slow Browsing Speeds Due to Onion Routing
One of the most notable drawbacks of Tor Browser is its impact on browsing speed. The multi-hop routing process, essential for maintaining anonymity, inherently reduces the speed of your internet connection.
Reasons for Slow Speeds:
- Multiple Relays: Each data packet passes through several relays, increasing latency.
- Network Congestion: Popular nodes can become congested, further slowing down traffic.
- Bandwidth Limitations: Volunteer-operated relays may have limited bandwidth, affecting overall performance.
Impact on Users:
- Reduced Efficiency: Activities requiring high-speed internet, such as streaming or large downloads, become impractical.
- User Experience: Slower load times can frustrate users accustomed to the rapid responsiveness of standard browsers.
| Factor | Effect on Tor Browser | Effect on Standard Browsers |
|---|---|---|
| Relay Hops | Increased latency | Minimal latency |
| Network Congestion | Frequent slowdowns | Generally stable performance |
| Bandwidth Availability | Limited by volunteer relays | High, centralized servers |
| Use Case Suitability | Suitable for browsing and research | Suitable for all types of internet use |
The inherent design of Tor Browser prioritizes security over speed, making it less suitable for bandwidth-intensive tasks.
Mitigating Slow Speeds:
- Select New Circuits: Refreshing your Tor circuit can sometimes connect you to faster relays.
- Optimize Settings: Adjust security settings to allow certain scripts that can enhance performance without significantly compromising security.
- Use Bridges: Connecting through bridges can bypass congested nodes and access less crowded pathways.
Despite these mitigation strategies, users should manage their expectations regarding the speed of Tor Browser, recognizing that enhanced privacy comes with trade-offs in performance.

Potential Risks of Accessing the Dark Web
Accessing the dark web through Tor Browser opens up a realm of resources and information but also exposes users to various risks and dangers.
Key Risks:
- Exposure to Illegal Content:
- Access to illicit marketplaces, illegal services, and prohibited content.
- Potential involvement in unlawful activities, leading to legal consequences.
- Malware and Scams:
- High prevalence of malicious websites distributing malware.
- Increased risk of encountering phishing schemes and fraudulent services.
- Vulnerability to Malicious Actors:
- Anonymity attracts hackers and cybercriminals aiming to exploit users.
- Potential for data theft and identity exposure if best practices are not followed.
Impact on Users:
- Legal Repercussions: Engaging with illegal content or activities can result in severe legal actions.
- Security Threats: Malware infections can compromise your device and personal data.
- Psychological Risks: Exposure to disturbing or harmful content can have adverse psychological effects.
| Risk Type | Description | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Illegal Content | Access to prohibited and illicit content | Avoiding engagement with illegal sites |
| Malware and Scams | High risk of downloading malicious software | Use antivirus, avoid unknown downloads |
| Malicious Actors | Cybercriminals targeting users | Employ strong security practices |
| Legal Repercussions | Severe penalties for illicit activities | Stay informed about legal boundaries |
Understanding these risks is essential for anyone planning to explore the dark web, as the potential dangers can have significant consequences.
Best Practices to Mitigate Risks:
- Stay Informed: Understand what constitutes illegal activities and avoid engaging with them.
- Use Security Tools: Employ reputable antivirus software and keep your system updated to protect against malware.
- Verify Sources: Only interact with trusted and verified websites and communities on the dark web.
- Maintain Anonymity: Avoid sharing any personal information that can link back to your real identity.
By adhering to these practices, users can navigate the dark web with a heightened awareness of the potential dangers, thereby minimizing the risks associated with its use.
How to Stay Safe While Using Tor
Ensuring your safety while using Tor Browser involves understanding its limitations and adopting best practices to protect your anonymity and security.
Safety Measures:
- Avoid Logging into Personal Accounts:
- Do not sign into accounts that can reveal your identity, such as email or social media.
- Creating separate anonymous accounts if necessary, but avoid linking them to personal information.
- Be Wary of Downloads:
- Only download files from trusted sources.
- Scan all downloads with updated antivirus software before opening them.
- Limit Browser Extensions:
- Refrain from adding additional plugins or extensions, as they can compromise your privacy.
- Stick to the privacy features provided by Tor Browser itself.
- Use Secure Connections:
- Always prefer HTTPS over HTTP to ensure encrypted communication.
- Tor Browser includes HTTPS Everywhere by default to enforce secure connections.
- Regularly Update Tor Browser:
- Keep your browser updated to benefit from the latest security patches and features.
- Enable automatic updates to ensure continuous protection.
Additional Tips:
- Disable JavaScript: Consider disabling JavaScript for higher security, though this may affect website functionality.
- Monitor Network Activity: Use tools to monitor unusual network activity that could indicate a security breach.
- Educate Yourself: Stay informed about the latest security threats and techniques to maintain anonymity online.
Best Practices Summary:
| Safety Measure | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Avoid Personal Logins | Prevents linking online activities to real identity | Maintains anonymity |
| Secure Downloads | Protects against malware and malicious software | Ensures device security |
| Limit Extensions | Reduces risk of privacy breaches from plugins | Enhances browser security |
| Use HTTPS Everywhere | Encrypts data between your browser and websites | Protects data integrity |
| Regular Updates | Keeps the browser secure with latest patches | Guards against vulnerabilities |
Implementing these safety measures significantly enhances your protection while using Tor Browser, ensuring a secure and anonymous browsing experience.
Troubleshooting and Common Issues with Tor Browser
While Tor Browser is designed to provide a secure and anonymous browsing experience, users may encounter various issues that require troubleshooting. Understanding common problems and their solutions can help maintain smooth and effective use of the browser.
Fixing Slow Performance and Connection Errors
Experiencing slow performance or connection errors can be frustrating when using Tor Browser. Here are steps to diagnose and resolve these issues:
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Restart Tor Browser:
- Sometimes, simply restarting the browser can resolve temporary connection glitches.
- Select a New Circuit:
- Click on the onion icon and choose “New Tor Circuit for this Site” to connect through different relays that may offer better performance.
- Check Firewall and Antivirus Settings:
- Ensure that your firewall or antivirus software is not blocking Tor Browser. Adjust settings to allow Tor traffic if necessary.
- Update Tor Browser:
- Running an outdated version can lead to bugs and security vulnerabilities. Always keep Tor Browser updated to the latest version.
- Use Bridges:
- If your ISP is restricting Tor traffic, using bridges can help bypass these restrictions and improve connectivity.
Additional Tips:
- Optimize Network Settings: Adjusting the number of relays your traffic uses can sometimes enhance speed.
- Reduce Load on Relays: Avoid peak usage times to minimize network congestion on popular relays.
- Limit Concurrent Activities: Closing unnecessary tabs and applications can free up bandwidth for Tor Browser.
Performance Enhancement Practices:
| Issue | Possible Solution | Steps to Resolve |
|---|---|---|
| Slow Browsing Speeds | Select a new circuit | Click onion icon > New Circuit |
| Connection Errors | Check firewall/antivirus settings | Allow Tor through security software |
| Outdated Browser | Update Tor Browser | Download latest version from official site |
| ISP Blocking | Use bridges | Configure bridges in Tor settings |
These troubleshooting steps address the most common performance and connectivity issues, ensuring that Tor Browser functions effectively.
Resolving CAPTCHA and Website Blocking Issues
Encountering CAPTCHAs or having websites block access when using Tor Browser is a common challenge. These measures are often implemented to prevent abuse and automated traffic.
Solutions to CAPTCHA and Blocking Issues:
- Disable JavaScript:
- While not always recommended for functionality, disabling JavaScript can reduce CAPTCHA prompts by limiting automated scripts.
- Lower Security Settings:
- Temporarily lowering security levels can allow certain website features to function correctly, reducing the likelihood of being blocked.
- Use a VPN in Conjunction with Tor:
- Combining a VPN with Tor can help bypass certain blocks and reduce the frequency of CAPTCHAs by masking Tor usage.
- Clear Cookies and Cache:
- Regularly clearing your browser’s cookies and cache can prevent websites from tracking your activity and prompting CAPTCHAs.
- Switch Exit Nodes:
- Changing your exit node can help if a particular node is frequently flagged by websites for suspicious activity.
Practical Tips:
- Avoid Frequent Requests: Make fewer simultaneous requests to minimize triggers for CAPTCHA systems.
- Consistent Browsing Patterns: Maintain consistent behavior to avoid being flagged as automated traffic.
- Use Alternative Access Methods: If a site continually blocks Tor traffic, consider accessing it through other secure methods or platforms.
CAPTCHA Resolution Techniques:
| Issue | Possible Solution | Implementation Steps |
|---|---|---|
| Excessive CAPTCHAs | Disable JavaScript | Settings > Security Level > Safest |
| Frequent Blocking | Lower security settings | Settings > Security Level > Safer |
| Legacy Node Flags | Change exit nodes | Click onion icon > New Circuit |
| Automated Traffic Detection | Limit rapid browsing actions | Browse more naturally, avoid scripts-heavy sites |
By applying these solutions, users can navigate around CAPTCHA and blocking challenges, maintaining access to desired websites without compromising their anonymity.
How to Ensure Full Anonymity While Using Tor
Achieving complete anonymity with Tor Browser requires adherence to certain best practices and avoidance of behaviors that could inadvertently reveal your identity.
Strategies for Maintaining Full Anonymity:
- Avoid Personal Logins:
- Do not log into personal accounts that are linked to your real identity, such as email, social media, or banking services.
- Do Not Download Files:
- Refrain from downloading files from untrusted sources, as they can contain malware or scripts that compromise anonymity.
- Use Anonymous Operating Systems:
- Consider using security-focused operating systems like Tails that are designed for anonymity and leave no traces on the device.
- Disable Browser Plugins:
- Turn off unnecessary plugins and extensions that could leak information about your browsing habits or device.
- Avoid Revealing Personal Information:
- Do not share personal details through forms, chats, or other online interactions that could link back to your real identity.
Additional Anonymity Enhancements:
- Use Anonymous Payment Methods: If engaging in transactions, use cryptocurrencies or other anonymous payment options.
- Regularly Change Circuits: Frequently changing your Tor circuit can further obscure your browsing patterns.
- Be Cautious with Communications: Use encrypted communication tools and avoid discussing identifiable information online.
Anonymity Best Practices:
| Practice | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Avoid Personal Logins | Prevents linking online activity to real identity | Maintains full anonymity |
| Use Security-Focused OS | Employs systems designed for privacy | Enhances overall security and anonymity |
| Disable Plugins | Blocks potentially invasive browser extensions | Reduces data leakage points |
| Anonymous Payment Methods | Utilizes cryptocurrencies for transactions | Protects financial anonymity |
Implementing these strategies ensures that your use of Tor Browser remains fully anonymous, safeguarding your identity against potential leaks and tracking.
Mindful Browsing:
Understanding the importance of each action taken while browsing can help maintain anonymity. Even seemingly harmless activities, like changing your display name or interacting with certain online communities, can have unintended consequences if not managed carefully.
FAQs
1. Is Tor Browser completely anonymous? While Tor Browser provides a high level of anonymity by routing your traffic through multiple relays, it is not infallible. Users must adhere to best practices to maintain privacy and avoid actions that could compromise their anonymity.
2. Can I use Tor Browser for streaming videos? Tor Browser is not optimized for high-bandwidth activities like streaming videos. The multiple relays and encryption processes inherently slow down your connection, making streaming impractical.
3. Is Tor usage detectable by my ISP? While Tor Browser conceals your browsing activity, your ISP can detect that you are using Tor but cannot see the specific sites you visit or your data. Using bridges can help hide Tor usage from your ISP.
4. Can Tor Browser protect me from malware? Tor Browser includes built-in protections such as NoScript and HTTPS Everywhere, which mitigate some malware risks. However, it is not a substitute for dedicated antivirus software. Always exercise caution when downloading files.
5. How often should I update Tor Browser? Regularly updating Tor Browser is crucial for maintaining security and privacy. Updates include important patches and improvements that protect against newly discovered vulnerabilities.
Key Takeaways
Enhanced Anonymity: Tor Browser uses onion routing to mask your IP address and encrypt your data, providing robust anonymity.
Access to Restricted Content: It allows users to bypass censorship and access both clearnet and dark web sites.
Comprehensive Privacy Features: Built-in tools like NoScript and HTTPS Everywhere protect against tracking and malicious scripts.
Performance Trade-offs: The increased privacy comes with slower browsing speeds due to the multiple relays.
Essential Safety Practices: Users must follow best practices, such as avoiding personal logins and being cautious with downloads, to maintain full anonymity.
Comparison with Other Browsers: Tor Browser offers superior anonymity compared to VPNs, Brave, and Firefox, but with trade-offs in speed and usability.
Potential Risks: Accessing the dark web can expose users to illegal content and security threats, necessitating cautious use.
Troubleshooting Tips: Common issues like slow performance and CAPTCHA challenges can be mitigated through specific adjustments and settings.
Conclusion
Tor Browser is a powerful tool for those who prioritize their privacy and anonymity online. By leveraging the Tor network’s onion routing technique, it offers unparalleled protection against tracking, surveillance, and censorship. While it comes with some limitations, such as slower browsing speeds and potential risks associated with accessing the dark web, the benefits it provides in safeguarding user privacy are significant. Whether you’re a journalist protecting your sources, an activist operating in restrictive environments, or an individual simply valuing your personal privacy, Tor Browser equips you with the means to navigate the internet securely and anonymously. By adhering to best practices and understanding its capabilities and limitations, you can make the most of what Tor Browser has to offer in today’s digitally monitored world.

